Biotin-Linked Polyclonal Antibody to Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) 
B-FGF; BFGF; FGFB; HBGH-2; Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor; Heparin-binding growth factor 2
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LAA551Hu71
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWB; IHC; ICC.If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryCytokineTumor immunityInfection immunity
- SourceAntibody labeling
- Ig Type IgG, Potency n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelBiotin
- Original Antibody n/a
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 500µg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against FGF2. It has been selected for its ability to recognize FGF2 in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.2-2µg/mL;1:250-2500
Immunohistochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:25-100
Immunocytochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:25-100
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
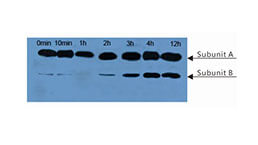 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- The influence of nutrients, biliary-pancreatic secretions, and systemic trophic hormones on intestinal adaptation in a Roux-en-Y bypass modelPubMed: 20438940
- Effect of heparan sulfate and gold nanoparticles on muscle development during embryogenesisPubMed: PMC3254262
- Effect of taurine and gold nanoparticles on the morphological and molecular characteristics of muscle development during chicken embryogenesisTandfonline: 644918
- Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) Enhances Engraftment and Angiogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Diabetic Hindlimb IschemiaPubmed: 22266669
- Electrospun Fibers with Plasmid bFGF Polyplex Loadings Promote Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic RatsPubmed: 22091745
- Antiangiogenic Activities of Cinnamon, Black and Green Tea Extracts on Experimentally Induced Breast Cancer in RatsScialert: Source
- Silver nanoparticles administered to chicken affect VEGFA and FGF2 gene expression in breast muscle and heart.PubMed: 22827927
- Carbon nanoparticles downregulate expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in the heart during embryogenesisPubMed: PMC3771850
- Nano-Nutrition of Chicken Embryos. The Effect of in Ovo Administration of Diamond Nanoparticles and L-Glutamine on Molecular Responses in Chicken Embryo Pectoral MusclesNCBI:PMC3856104
- Nano-nutrition of chicken embryos. The effect of silver nanoparticles and ATP on expression of chosen genes involved in myogenesisPubmed: 23952606
- Role of sensory and motor intensity of electrical stimulation on fibroblastic growth factor-2 expression, inflammation, vascularization, and mechanical strength of full-thickness woundsPubmed: 23934870
- Carboxypeptidase E-ΔN, a Neuroprotein Transiently Expressed during Development Protects Embryonic Neurons against Glutamate NeurotoxicityPubmed:25426952
- Effects of Hemostatic Agents on Fibroblast CellsLww:Source
- bFGF-grafted electrospun fibrous scaffolds via poly(dopamine) for skin wound healingRsc:Source
- Effect of silver nanoparticles and hydroxyproline, administered in ovo, on the development of blood vessels and cartilage collagen structure in chicken embryosPubmed:25530495
- The effects of self-assembling peptide RADA16 hydrogel on malignant phenotype of human hepatocellular carcinoma cellPubMed: 26628972
- Evaluation of Changes in Doppler Ultrasonography Indices and Levels of Maternal Serum Angiogenic Factors throughout Pregnancy in EwesScience: Article
- Hypoxia-induced secretion of IL-10 from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell promotes growth and cancer stem cell properties of Burkitt lymphomaPubMed: 26695151
- Preparation and characterization of pro-angiogenic gel derived from small intestinal submucosaarticle:S1742706115301410
- Surface biofunctional drug-loaded electrospun fibrous scaffolds for comprehensive repairing hypertrophic scarsPubmed:26774564
- Changes in growth factor levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of autism patients after transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cellsPubmed:27323064
- 3-O-Methyldopa inhibits astrocyte-mediated dopaminergic neuroprotective effects of l-DOPApubmed:27456338
- 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid-Based Photodynamic Therapy Restrains Pathological Hyperplasia of Fibroblasts898221
- FGF-2-mediated FGFR1 signaling in human microvascular endothelial cells is activated by vaccarin to promote angiogenesispubmed:28841454
- 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid-Based Photodynamic Therapy Restrains Pathological Hyperplasia of Fibroblastspubmed:28052053
- Platelet-derived growth factor and stromal cell-derived factor-1 promote the skin wound repairing effect of bone mesenchymal stem cells: a key role of matrix metalloproteinase 1 and collagensISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058424
- The Combination of Acellular Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa (SIS) Cryogel Granules and Adipose Tissue Improves the Survival Ratio of Fat Grafting in Mice10.1166/jbt.2017.1652
- Lower Senescence of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells than Donor-Matched Bone Marrow Stem Cells for Surgical Ventricular RestorationPubmed:29630447
- Increased serum FGF2 levels in first-episode, drug-free patients with schizophreniaPubmed: 30172685
- Silencing of Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cellsPubmed: 30359541
- Gene-activating skin substitute comprised of PLLA/POSS nanofibers and plasmid DNAs encoding ANG and bFGF promotes in vivo revascularization and …
- HOXA9 is a novel myopia risk genePubmed: 30674274
- Immunomodulated electrospun fibrous scaffolds via bFGF camouflage for pelvic regeneration
- A novel xeno-free culture system for human retinal pigment epithelium cellsPubmed: 31024807
- Low Degree Hyaluronic Acid Crosslinking Inducing the Release of TGF-Β1 in Conditioned Medium of Wharton's Jelly-Derived Stem Cells
- Bisphenol S triggers the malignancy of hemangioma cells via regulation of basic fibroblast growth factorPubmed: 31669319
- β-Galactosylceramidase Deficiency Causes Bone Marrow Vascular Defects in an Animal Model of Krabbe DiseasePubmed: 31905906
- Long non‑coding RNA NORAD regulates angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via miR‑590‑3p under hypoxic conditionsPubmed: 32323787
- Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor is Involved in Bisphenol S Induced Proliferation of Hemangioma Cells
- New design to remove leukocytes from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) based on cell dimension rather than density33842739
- Highly interconnected inverse opal extracellular matrix scaffolds enhance stem cell therapy in limb ischemia33878473
- Double Layer Composite Membrane for Preventing Tendon Adhesion and Promoting Tendon Healing33812576
- Ratlarda deneysel kolon anastomoz ka?a?? modelindeintraperitoneal atorvastatin uygulamas?n?n anastomozka?a?? onar?m? ¨¹zerine etkisi
- Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 and fibroblast growth factor 21 in alcohol-induced liver cirrhosisPubmed:35070009
- Human adipose-derived stem cell-loaded small intestinal submucosa as a bioactive wound dressing for the treatment of diabetic wounds in rats





