- Featured-Product
ELISA Kit for Ferritin (FE) 
- UOM
- FOB US$ 266.00 US$ 380.00 US$ 1,710.00 US$ 3,230.00 US$ 26,600.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SEA518Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayTumor immunityHematology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Ferritin (FE) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Ferritin (FE) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 79-97 | 90 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 83-99 | 93 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 83-102 | 95 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Ferritin (FE) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Ferritin (FE) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Ferritin (FE) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 78-96% | 96-103% | 91-103% | 87-99% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 89-102% | 78-88% | 93-101% | 79-93% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 90-101% | 94-105% | 88-96% | 97-104% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

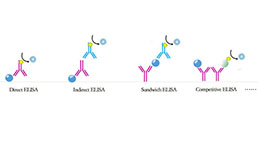
Test principle
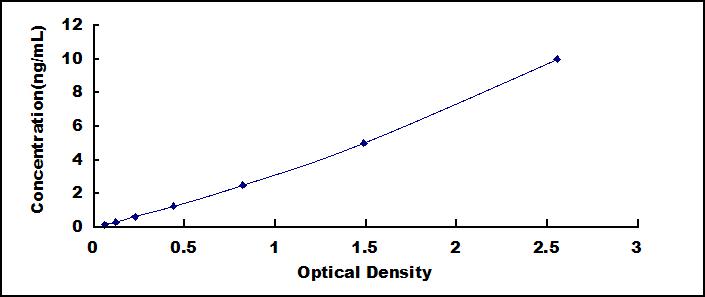
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Ferritin (FE). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Ferritin (FE). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain Ferritin (FE), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of Ferritin (FE) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- PGC-1α regulates hepatic hepcidin expression and iron homeostasis in response to inflammation.Pubmed: 23438894
- Redox-regulation of gelatinases during growth of cisplatin-sensitive and resistant Guerin carcinoma.PubMed: 25804229
- Host H68D Genotype Affects Tumor Growth in Mouse MelanomaOpen-Access: 1948-5956-1000353
- The effects of polysaccharides from the root of Angelica sinensis on tumor growth and iron metabolism in H22-bearing micePubmed:26757699
- The Labile Iron Pool in Monocytes Reflects the Activity of the Atherosclerotic Process in Men with Chronic Cardiovascular Diseasepubmed:27782743
- 4 (th) Mediterranean Multidisciplinary Course on Iron Anemia April 29 (th)-30 (th) 2016, Madrid, Spain.pubmed:27615544
- Acidic Polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis Reverses Anemia of Chronic Disease Involving the Suppression of Inflammatory Hepcidin and NF-κB Activationpubmed:29147463
- sucrosomial® iron absorption studied by in vitro and ex-vivo modelspubmed:29055735
- In vitro assessment of bio-augmented minerals from peanut oil cakes fermented by Aspergillus oryzae through Caco-2 cells.pubmed:29051659
- Anemia and Iron Deficiency Related to Inflammation, Helicobacter pylori Infection and Adiposity in Reproductive-age Cuban Women10.1590/MEDICC.2017.1902030004
- The Role of Insulin Therapy in Correcting Hepcidin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.pubmed:28584599
- Preparation of lactose-iron complex and its cyto-toxicity, in-vitro digestion and bioaccessibility in Caco-2 cell model system10.1016/j.fbio.2017.10.001
- Long-Term Dexamethasone Exposure Down-Regulates Hepatic TFR1 and Reduces Liver Iron Concentration in Ratspubmed:28629118
- Physicochemical characterization of mineral (iron/zinc) bound caseinate and their mineral uptake in Caco-2 cellsPubmed:29622185
- Super-dosing phytase improves the growth performance of weaner pigs fed a low iron diet10.1016:j.anifeedsci.2018.01.012
- Iron homeostasis in pregnancy and spontaneous abortionPubmed: 30394565
- Assessment of iron deficiency anaemia and its risk factors among adults with chronic kidney disease in a tertiary hospital in Nigeria
- New thiazolidinones reduce iron overload in mouse models of hereditary hemochromatosis and β-thalassemiaPubmed: 30792208
- PHYSIOLOGICAL ADAPTATIONS TO HEAT ACCLIMATION; REPERCUSSIONS ON CYCLING PERFORMANCE
- Synthesis, characterization and cellular mineral absorption of nanoemulsions of Rhododendron arboreum flower extracts stabilized with gum arabic
- Transferrin plays a central role in coagulation balance by interacting with clotting factorsPubmed: 31811276
- Gum arabic capped copper nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and applicationsPubmed: 31904465
- Improvement of Mineral Absorption and Nutritional Properties of Citrullus vulgaris Seeds Using Solid-State FermentationPubmed: 32255407
- Whey protein-iron or zinc complexation decreases pro-oxidant activity of iron and increases iron and zinc bioavailability
- Systemic iron deficiency does not affect the cardiac iron content and progression of heart failure34139233
- The mechanism of the imbalance between proliferation and ferroptosis in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells based on the activation of SLC7A11Pubmed:35700835