Monoclonal Antibody to Surfactant Protein C (SP-C) 
SFTPC; PSP-C; SFTP2; SPC; SP5; Surfactant Associated Protein C; Pulmonary Surfactant Protein C; Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Val)
Overview
Properties
- Product No.MAB623Ra21
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWB; IHC; ICC; IP.
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryTumor immunityInfection immunityPulmonology
- SourceMonoclonal antibody preparation, Host Mouse
- Ig Isotype IgG, Clone Number n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen n/a
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 1mg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against SP-C. It has been selected for its ability to recognize SP-C in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.2-2µg/mL;1:500-5000
Immunohistochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:50-200
Immunocytochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:50-200
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
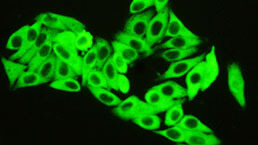 Antibody Labeling Customized Service
Antibody Labeling Customized Service
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- Detection of surfactant proteins A, B, C, and D in human nasal mucosa and their regulation in chronic rhinosinusitis with polypsPubMed: 23406594
- Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Express and Secrete Human Surfactant ProteinsPubMed: PMC3551896
- The Detection of Surfactant Proteins A, B, C and D in the Human Brain and Their Regulation in Cerebral Infarction, Autoimmune Conditions and Infections of the CNSPubMed: PMC3787032
- Nachweis und Charakterisierung des Oberfl?chenproteins PLUNC (Palate, Lung and Nasal Clone Protein) an der Augenoberfl?che und Bedeutung für das Trockene AugeOpus4:Source
- Autophagy regulates hyperoxia-induced intracellular accumulation of surfactant protein C in alveolar type II cellsPubMed: 26122393
- Serum Levels of Surfactant Proteins in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (CPFE)Pubmed:27337142
- The Cerebral Surfactant System and Its Alteration in HydrocephalicConditions.pubmed:27656877
- Correlations of Ventricular Enlargement with Rheologically Active SurfactantProteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid.pubmed:28101052
- Correlations of Ventricular Enlargement with Rheologically Active Surfactant Proteins in Cerebrospinal FluidPMC5209370
- Chronic lung injury and impaired pulmonary function in a mouse model of acid ceramidase deficiency.pubmed:29167126
- Effects and molecular mechanisms of intrauterine infection/inflammation on lung developmentPubmed:29747649
- Serum Surfactant Protein Levels in Patients Admitted to the Hospital with Acute COPD ExacerbationPubmed:29445934
- Rheologically Essential Surfactant Proteins of the CSF Interacting with Periventricular White Matter Changes in Hydrocephalus Patients–Implications for CSF …Doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01648-z
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Have the Ability to Differentiate into Alveolar Epithelial Cells and Ameliorate Lung Injury Caused by Elastase-Induced Emphysema …
- Efficient Differentiation of Mouse Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Alveolar Epithelium Type II with a BRD4 InhibitorPubmed: 31949433





