Brain Astrocytes (BA)
Astroglia; Astrocytic glial cells
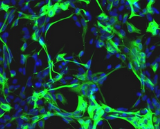
Astrocytes are a sub-type of glial cells in the central nervous system. They are also known as astrocytic glial cells. Star-shaped, their many processes envelop synapses made by neurons. Astrocytes are classically identified using histological analysis; many of these cells express the intermediate filament glial fibrillary acidic protein.
The radial glia are disposed in planes perpendicular to axis of ventricles. One of their processes abuts the pia mater, while the other is deeply buried in gray matter. Radial glia are mostly present during development, playing a role in neuron migration. Müller cells of retina and Bergmann glia cells of cerebellar cortex represent an exception, being present still during adulthood. When in proximity to the pia mater, all three forms of astrocytes send out processes to form the pia-glial membrane.Brain astrocytes are isolated from brain tissue.
Organism species: Homo sapiens (Human)
- Cell CSI011Hu01 Primary Human Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Extract of Brain Astrocytes (BA) Total Protein/DNA/RNA Extract Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Medium for Brain Astrocytes (BA) (If Necessary) Cell Culture Medium Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Cell CSI011Mu01 Primary Mouse Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Extract of Brain Astrocytes (BA) Total Protein/DNA/RNA Extract Customized Service Offer
- Medium MSI011Mu11 Medium for Mouse Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
Organism species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Cell CSI011Ra01 Primary Rat Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Extract of Brain Astrocytes (BA) Total Protein/DNA/RNA Extract Customized Service Offer
- Medium MSI011Ra11 Medium for Rat Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
Organism species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Cell CSI011Rb01 Primary Rabbit Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Extract of Brain Astrocytes (BA) Total Protein/DNA/RNA Extract Customized Service Offer
- Medium MSI011Rb11 Medium for Rabbit Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
Organism species: Canis familiaris; Canine (Dog)
- Cell CSI011Ca01 Primary Canine Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Extract of Brain Astrocytes (BA) Total Protein/DNA/RNA Extract Customized Service Offer
- Medium MSI011Ca11 Medium for Canine Brain Astrocytes (BA) In Stock


