Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
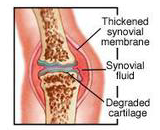
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation in one or more joints.There are over 100 different forms of arthritis.The most common form of arthritis is osteoarthritis, a result of trauma to the joint, infection of the joint, or age. Other arthritis forms are rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and related autoimmune diseases. Septic arthritis is caused by joint infection. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints.
Models for rheumatoid arthritis can be used to aid in understanding the mechanism of action of novel anti-inflammatory compounds. Adjuvant administration induced polyarticular and systemic inflammation, which included spleen and liver. In the liver, multifocal hepatic granulomas were observed. Studies indicate that arthritis model is accompanied by an initial increased release of excitatory amino acids (EAA's) at the time of injection which is dependent on the activation of both non-NMDA and NMDA receptors.
Organism species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Disease model DSI522Mu01 Mouse Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Disease model DSI522Mu03 Mouse Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Disease model DSI522Ra01 Rat Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Disease model DSI522Ra03 Rat Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Tissue TSI522Ra65 Rat Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Tissue TSI522Ra67 Rat Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Cavia (Guinea pig )
- Disease model DSI522Gu02 Cavia Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Disease model DSI522Gu01 Cavia Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Disease model DSI522Gu03 Cavia Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Disease model DSI522Rb02 Rabbit Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Disease model DSI522Rb01 Rabbit Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Canis familiaris; Canine (Dog)
- Customized Service n/a Model for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Disease Model Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer


