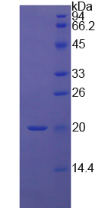
Active Midkine (MK) 
MDK; ARAP; NEGF2; Neurite Growth-Promoting Factor 2; Amphiregulin-associated protein; Midgestation and kidney protein; Neurite outgrowth-promoting factor 2
- UOM
- FOB US$ 340.00 US$ 850.00 US$ 1,700.00 US$ 5,100.00 US$ 12,750.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA631Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategorySignal transductionTumor immunityDevelopmental science
- Buffer Formulation20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point9.4
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test

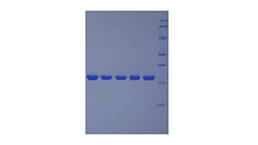
Figure. The binding activity of MK with LRP1.<br/>Midkine (MK) also known as neurite growth-promoting factor 2 (NEGF2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MDK gene. MK is a basic heparin-binding growth factor of low molecular weight, and forms a family with pleiotrophin. It is pleiotropic, capable of exerting activities such as cell proliferation, cell migration, angiogenesis and fibrinolysis. MK may potentially be indirectly targeted as a cancer treatment as a result of its cancerous proliferation properties. Besides, Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Related Protein 1 (LRP1) has been identified as an interactor of MK, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human MK and recombinant human LRP1. Briefly, MK were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100uL were then transferred to LRP1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-MK pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of MK and LRP1 was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Usage
Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl (pH8.0) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Immunochemical Methods for the Detection of Midkine in Samples of Human OriginSpringer: Source
- Midkine Controls Arteriogenesis by Regulating the Bioavailability of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase 1 and …10.1016:j.ebiom.2017.11.020
- Midkine Promotes Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation Through Its Pro-Inflammatory, Angiogenic and Anti-Apoptotic Functions in Apolipoprotein E-Knockout Micepubmed:28781288
- Midkine Controls Arteriogenesis by Regulating the Bioavailability of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A and the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase 1 and …Pubmed:29233575
- Clinical value of jointly detection pleural fluid Midkine, pleural fluid adenosine deaminase, and pleural fluid carbohydrate antigen 125 in the identification of nonsmall …Pubmed:29797475
- Charakterisierung der funktionalen Rolle des Zytokins Midkine bei der Arteriogenese:
- The possible role of Dickkopf-1, Golgi protein-73 and Midkine as predictors of hepatocarcinogenesis: a review and an Egyptian studyPubmed: 32198440
- Effects of different pulp-capping materials on cell death signaling pathways of lipoteichoic acid-stimulated human dental pulp stem cellsPubmed: 33206337