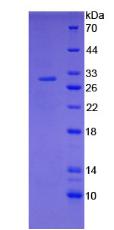
Active Tissue Factor (TF) 
CD142; FIII; F3; TFA; Thromboplastin; Coagulation Factor III
- UOM
- FOB US$ 368.00 US$ 920.00 US$ 1,840.00 US$ 5,520.00 US$ 13,800.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA524Ra01
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryHematologyCardiovascular biology
- Buffer Formulation20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point9.2
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
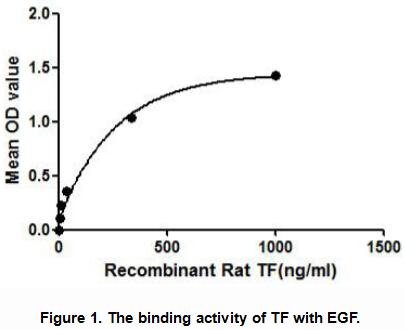
TF (Tissue factor) also known for platelet tissue factor, factor III, thromboplastin, or CD142, is a cell surface glyprotein present in subendothelial tissue and leukocytes. TF is necessary for the initiation of thrombin formation from the zymogen prothrombin. It has been proven that EGF can bind with the TF on the hemangioendotheliocytes. Thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant rat TF and recombinant rat EGF. Briefly, TF were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01%BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100uL TF were then transferred to EGF-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-TF pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of TF and EGF was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Usage
Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl (pH8.0) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Calcitonin gene-related peptide-mediated antihypertensive and anti-platelet effects by rutaecarpine in spontaneously hypertensive ratsPubMed: 18625276
- Increased plasma level of asymmetric dimethylarginine in hypertensive rats facilitates platelet aggregation: role of plasma tissue factorNrcresearchpress: y10-115
- Ruscogenin attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in ratsPubmed: 23538027
- Endothelial gene expression and molecular changes in response to radiosurgery in in vitro and in vivo models of cerebral arteriovenous malformationsPubmed: 24199192
- Sphingolipid Pathway Regulates Innate Immune Responses at the Fetomaternal Interface during PregnancyPubmed:25505239
- Thrombosis in Hemodialysis Patients; Their Association with Tissue Factor and Tissue Factor Pathway InhibitorPubMed: 20011089
- Noble-Collip Drum Trauma Induces Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation But Not Acute Coagulopathy of Trauma-ShockPubMed: 25423126
- Ex vivo simulation of cardiopulmonary bypass with human blood for hemocompatibility testingPubMed: 26243277
- Trans‐fatty acid promotes thrombus formation in mice by aggravating antithrombogenic endothelial functions via Toll‐like receptorsPubMed: 25546502
- The effects of polysaccharides from the root of Angelica sinensis on tumor growth and iron metabolism in H22-bearing micePubmed:26757699
- Nebulized Heparin Attenuates Pulmonary Coagulopathy and Inflammation through Alveolar Macrophages in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injurypubmed:29202212
- Nebulized anti-coagulants as a therapy for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndromePubmed: 29202212
- Effects of nebulized antithrombin and heparin on inflammatory and coagulation alterations in an acute lung injury model in ratsPubmed: 31755229
- Amelioration of Coagulation Disorders and Inflammation by Hydrogen-Rich Solution Reduces Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats through NF-κB …Pubmed: 32587471
- Effect of Glucocorticoid Administration in Intravenous Pulses on Selected Parameters of the Coagulation SystemPubmed:35685509