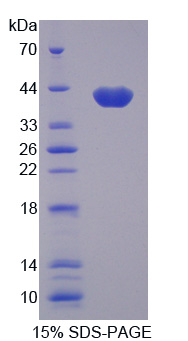
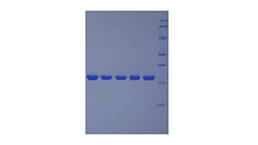
Recombinant Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) 
Apo-C1; Truncated apolipoprotein C-I
Overview
Properties
- Product No.RPA252Rb01
- Organism SpeciesOryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit) Same name, Different species.
-
Applications
Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB.
If bio-activity of the protein is needed, please check active protein.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathway
- Source Prokaryotic expression, Host E.coli
- Endotoxin Level<1.0EU per 1µg (determined by the LAL method)
- Subcellular LocationSecreted
- Molecular Mass 37.0kDa, Accurate 40kDa(Analysis of differences refer to the manual)
- Residues & TagsPro28~Ser87 with N-terminal His and GST Tag
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 97%
- Isoelectric Point8.62
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
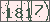
Sequence
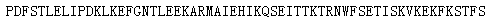
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit
Endotoxin Removal Kit
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Protein Labeling Customized Service
Protein Labeling Customized Service
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Recombinant Protein Customized Service
Recombinant Protein Customized Service
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit II
Endotoxin Removal Kit II
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Proteomic and genomic analyses suggest the association of Apolipoprotein C1 with abdominal aortic aneurysmOnlinelibrary: prca.201300119
- Colostrum and milk protein rankings and ratios of importance to neonatal calf health using a proteomics approachpubmed:28189329
- The HDL from septic-ARDS patients with composition changes exacerbates pulmonary endothelial dysfunction and acute lung injury induced by cecal ligation …Pubmed: 33148285