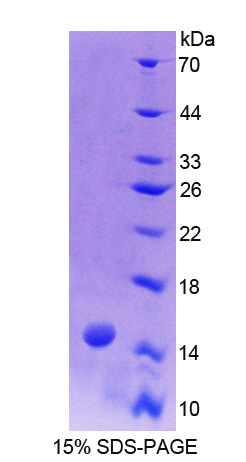
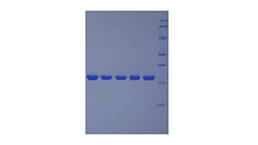
Recombinant Biglycan (BGN) 
DSPG1; PG-S1; PGI; SLRR1A; Biglycan Proteoglycan; Bone/cartilage proteoglycan I
Overview
Properties
- Product No.RPJ226Hu02
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
-
Applications
Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB.
If bio-activity of the protein is needed, please check active protein.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryReproductive science
- Source Prokaryotic expression, Host E.coli
- Endotoxin Level<1.0EU per 1µg (determined by the LAL method)
- Subcellular LocationSecreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix
- Molecular Mass 17.3kDa, Accurate 17kDa(Analysis of differences refer to the manual)
- Residues & TagsThr230~Tyr366 (Accession # P21810) with
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point7.9
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
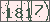
Sequence
Usage
Reconstitute in PBS or others.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit
Endotoxin Removal Kit
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Protein Labeling Customized Service
Protein Labeling Customized Service
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Recombinant Protein Customized Service
Recombinant Protein Customized Service
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
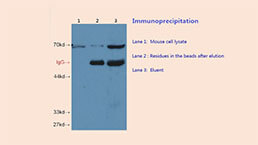 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit II
Endotoxin Removal Kit II
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Tumour endothelial cells in high metastatic tumours promote metastasis via epigenetic dysreCavia (Guinea pig )lation of biglycanPubmed:27295191
- Tenomodulin is essential for prevention of adipocyte accumulation and fibrovascular scar formation during early tendon healing.pubmed:29022912
- Degenerative aortic valve disease and diabetes: Implications for a link between proteoglycans and diabetic disorders in the aortic valvePubmed: 30563371
- Die Rolle der extrazellulären Matrix in der degenerativen Aortenklappenerkrankung unter dem Einfluss von Diabetes
- Multi-omic signatures of atherogenic dyslipidaemia: pre-clinical target identification and validation in humans33407555
- Inhibition of Stromal Biglycan Promotes Normalization of the Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Chemotherapeutic Efficacy33966638