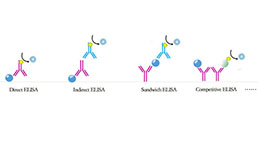
ELISA Kit DIY Materials for Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (gABA) 
4-Aminobutyric Acid
- UOM
- FOB US$ 1,211.00 US$ 2,019.00 US$ 3,634.00 US$ 7,067.00 US$ 12,114.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.KSA900Ge11
- Organism SpeciesPan-species (General) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsMain materials for "Do It (ELISA Kit) Yourself".
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategorySignal transductionCardiovascular biologyNeuro scienceBone metabolism
- Reagent Contents Capture Antibody, Biotin-labeled Competitor, Standard, Streptavidin-HRP, TMB Substrate, 96-well Plate
- Detectable Sampleserum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Applicable PrincipleCompetitive Inhibition ELISA for Antigen Detection
- Detectable Range24.69-2000pg/mL
- Applicable Sensitivity9.27pg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The Abs in the kit have high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (gABA). No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (gABA) and analogues was observed.
Usage
1. Coat the plates with 100μL per well of working solution of Capture Antibody.incubate overnight at 4°C or incubate at 37°C for 2 hours.
2. Aspirate and wash 1 time.
3. Block the plates with 200 μL per well of working solution of Blocking Buffer. Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 hours.
4. Aspirate and wash 1 time. The plates are now ready for sample detection, the protocol is the same as regular ELISA.
Storage
Antibodies, Standard and Streptavidin-HRP should be stored at -20°C. TMB should be stored at 4°C. 96-well Plate could be stored at room temperature. The contents are valid for twelve months. They are stable for one month after opening when stored at 4°C.
Support pack
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Effect of sub-acute exposure to acrylamide on GABAergic neurons and astrocytes in weaning rat cerebellumPubMed: 21444355
- Expression of the neuron-specific potassium chloride cotransporter KCC2 in adult rat cochlear.PubMed: 18577424
- Decreased Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Associated with HMGB1 and Increased Hyperactivity in Children with AutismPubMed: PMC3623607
- Correlation Between Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Plasma Levels in Autistic ChildrenPubMed: PMC3694825
- Decreased Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) and Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) in Individuals with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)PubMed: PMC3762604
- Renal Denervation Improves the Baroreflex and GABA System in Chronic Kidney Disease-induced Hypertensionpubmed:27917928
- Sex differences in the glutamate signaling pathway in juvenile ratsPubmed:28861894
- A novel homozygous mutation in GAD1 gene described in a schizophrenic patient impairs activity and dimerization of GAD67 enzymePubmed: 30341396
- Aucubin Alleviates Seizures Activity in Li-Pilocarpine-Induced Epileptic Mice: Involvement of Inhibition of Neuroinflammation and Regulation of NeurotransmissionPubmed: 30666488
- Differentiation of human glioblastoma U87 cells into cholinergic neuronPubmed: 30928478
- Glutamate Signaling Defects in Propionic Acid Orally Administered to Juvenile Rats as an Experimental Animal Model of Autism
- Effect of gamma radiation on combination therapy of certain antiepileptic drugs in rats.
- Antiepileptic effects of exogenous β‑hydroxybutyrate on kainic acid‑induced epilepsyPubmed: 33101467
- Dementia model mice exhibited improvements of neuropsychiatric symptoms as well as cognitive dysfunction with neural cell transplantation33828024
- Age-dependent neurological phenotypes in a mouse model of PRRT2-related diseases34101060
- Overexpression of wild-type human amyloid precursor protein alters GABAergic transmission34475508
- Adaptogenic potential of ginsenosides against domoic acid‐induced toxicity by regulating neuronal stress and kinate receptors: Ex vivo and in silico studiesPubmed:35102569