CLIA Kit for Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) 
CD254; TNFSF11; ODF; OPGL; TRANCE; HRANKL2; SOdf; Tumor Necrosis Factor(ligand)superfamily Member 11; TNF-related activation-induced cytokine
- UOM
- FOB US$ 588.00 US$ 840.00 US$ 3,780.00 US$ 7,140.00 US$ 58,800.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SCA855Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsChemiluminescent immunoassay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategorySignal transductionMetabolic pathwayApoptosisTumor immunityBone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 90-97 | 93 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 96-103 | 101 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-90 | 83 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 80-95% | 92-102% | 99-105% | 92-102% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 94-102% | 99-105% | 84-104% | 89-96% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 80-101% | 83-101% | 89-103% | 86-93% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Substrate A | 1×10mL | Substrate B | 1×2mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 100µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10 minutes at 37°C;
8. Read RLU value immediately.
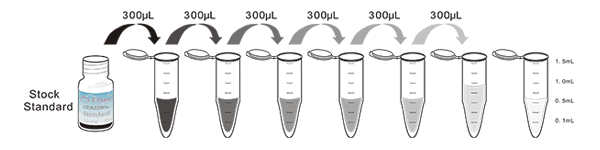
Test principle
The microplate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microplate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. Then the mixture of substrate A and B is added to generate glow light emission kinetics. Upon plate development, the intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the Receptor Activator Of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand (RANkL) level in the sample or standard.;
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 CLIA Kit Customized Service
CLIA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution -
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Citations
- Compressive stress induced the up-regulation of M-CSF, RANKL, TNF-α expression and the down-regulation of OPG expression in PDL cells via the integrin-FAK pathwayScienceDirect: S0003996912003998
- Adipokines in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients: The Correlations with Osteoclast Precursors and Bone ErosionsPubMed: PMC3483160
- Regulatory effect of calcineurin inhibitor, tacrolimus, on IL-6/sIL-6R-mediated RANKL expression through JAK2-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytesPubMed: PMC3672788
- The effects of chronic zoledronate usage on the jaw and long bones evaluated using RANKL and osteoprotegerin levels in an animal modelPubmed: 23522850
- Estrogen deficiency does not decrease the in vitro osteogenic potential of rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cellsPubmed: 24687841
- Effects and mechanisms of 8-prenylnaringenin on osteoblast MC3T3-E1 and osteoclast-like cells RAW264.7Onlinelibrary: fsn3.109
- Effects and mechanisms of 8‐prenylnaringenin on osteoblast MC3T3‐E1 and osteoclast‐like cells RAW264. 7Pubmed:Pmc4221832
- Effect of Nicotine on RANKL and OPG and Bone Mineral DensityPubmed:24830656
- Effects of icariin on the regulation of the OPG?RANKL?RANK system are mediated through the MAPK pathways in IL?1β?stimulated human SW1353 chondrosarcoma …Pubmed:25270538
- Carvedilol promotes neurological function, reduces bone loss and attenuates cell damage after acute spinal cord injury in ratsPubmed:25424914
- A novel model of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in ratsPubMed: 26191212
- MicroRNA-106b inhibits osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis by targeting RANKL in giant cell tumor of bonePubMed: 26053181
- Serum osteopontin levels are upregulated and predict disability after an ischaemic strokePubMed: 25845543
- Effetti del laser a bassa dose su cellule osteoblasticheINCERTIPARENTI_SERENA_TESI.pdf
- Noni leaf and black tea enhance bone regeneration in estrogen-deficient rats.pubmed:27908549
- Extracorporeal shock waves alone or combined with raloxifene promote bone formation and suppress resorption in ovariectomized rats.pubmed:28158228
- The effect of lamotrigine and phenytoin on bone turnover and bone strength: A prospective study in Wistar ratspubmed:27838501
- Odontoclastogenesis of mouse papilla-derived MDPC-23 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide.pubmed:28333374
- Sprint Interval Training Induces A Sexual Dimorphism but does not Improve Peak Bone Mass in Young and Healthy Mice.pubmed:28303909
- Skeletal Site-specific Effects of Zoledronate on in vivo Bone Remodeling and in vitro BMSCs Osteogenic Activity.pubmed:28139685
- Anti-osteoporotic effects of an antidepressant tianeptine on ovariectomized ratsS0753332216322752
- SAT0003 The Role of 12/15-Lipoxygenase in The Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis in Micecontent:75
- Allogeneic yet major histocompatibility complex‑matched bone marrow transplantation in mice results in an impairment of osteoblasts and a significantly reduced trabecular bonearticle:10.1007
- Assessment of bone metabolism and biomechanical properties of the femur, following treatment with anastrozole and letrozole in an experimental model of menopauseol.2017.6596
- Peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor γ plays dual roles on experimental periodontitis in ratsPubmed:29574908
- Effect of long-term administration of mangiferin from on bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats10.1016:j.jff.2018.04.048
- Switched memory B cells promote alveolar bone damage during periodontitis: An adoptive transfer experimentPubmed:30015235
- The effect of levetiracetam on rat bone mineral density, bone structure and biochemical markers of bone metabolismPubmed:29428468
- Allogeneic yet major histocompatibility complex-matched bone marrow transplantation in mice results in an impairment of osteoblasts and a significantly reduced …Pubmed:28766138
- Liraglutide exerts a bone‑protective effect in ovariectomized rats with streptozotocin‑induced diabetes by inhibiting osteoclastogenesisPubmed:29805533
- The sole and combined effect of simvastatin and platelet rich fibrin as a filling material in induced bone defect in tibia of albino ratsPubmed: 30208342
- Improved RANKL expression and osteoclastogenesis induction of CD27+ CD38− memory B cells: A link between B cells and alveolar bone damage in periodontitisPubmed: 30346027
- NUMB maintains bone mass by promoting degradation of PTEN and GLI1 via ubiquitination in osteoblastsPubmed: 30455992
- Alendronate Effect in RANKL Concentration at Ovariectomized Sprague Dawley Rat.
- Development and characterization of supramolecular calcitonin assembly and assessment of its interactions with the bone remodelling processPubmed: 30797058
- Evaluation of therapeutic effects of teriparatide in a rat model of zoledronic acid-induced bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis
- Comparison of RANKL expression, inflammatory markers, and cardiovascular risk in patients with acute coronary syndrome with and without rheumatoid arthritisPubmed: 31297563
- Regulation of JAK/STAT signal pathway by miR-21 in the pathogenesis of juvenile idiopathic arthritisPubmed: 31641939
- Mice lacking plastin-3 display a specific defect of cortical bone acquisitionPubmed: 31678489
- IL-38 restrains inflammatory response of collagen-induced arthritis in rats via SIRT1/HIF-1α signaling pathwayPubmed: 32347300
- Anti-osteoporosis effect of Semen Cuscutae in ovariectomized mice through inhibition of bone resorption by osteoclasts34801609
- Inducible T‐cell co‐stimulator (ICOS) and ICOS ligand are novel players in the multiple‐myeloma microenvironmentPubmed:34954822
- Jiangu granule ameliorated OVX rats bone loss by modulating gut microbiota-SCFAs-Treg/Th17 axisPubmed:35453007
- Transcriptomic profiling revealed the role of apigenin-4′-O-α-L-rhamnoside in inhibiting the activation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via MAPK …Pubmed:35660352
- Identification of marker proteins in preterm and term birth: Relationship of rankl and HSP70 in the cord blood