ELISA Kit for Pepsin (PP) 
- UOM
- FOB US$ 490.00 US$ 700.00 US$ 3,150.00 US$ 5,950.00 US$ 49,000.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SEA632Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseMetabolic pathwayTumor immunityGastroenterology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Pepsin (PP) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Pepsin (PP) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 78-95 | 87 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-92 | 87 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 98-105 | 102 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Pepsin (PP) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Pepsin (PP) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Pepsin (PP) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 84-92% | 79-95% | 80-89% | 80-94% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 79-97% | 91-98% | 78-89% | 81-99% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 98-105% | 93-101% | 87-104% | 93-105% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

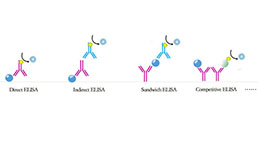
Test principle
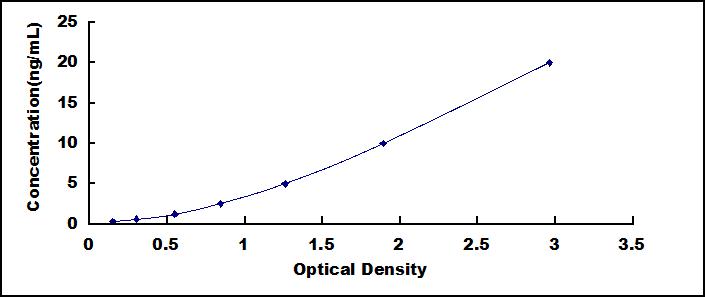
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Pepsin (PP). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Pepsin (PP). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain Pepsin (PP), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of Pepsin (PP) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- LEVEL OF PEPSIN AND BILE ACIDS IN THE SALIVA OF PATIENTS WITH GLOTTIS T1 CARCINOMASzd:Source
- Higher levels of total pepsin and bile acids in the saliva as a possible risk factor for early laryngeal cancerPubmed:Pmc4362607
- Pepsin and bile acids in saliva in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux – a prospective comparative studyPubMed: 25516364
- Does Positioning Affect Tracheal Aspiration of Gastric Content in Ventilated Infants?PubMed: 25313850
- Detecting Laryngopharyngeal Reflux by Immunohistochemistry of Pepsin in the Biopsies of Vocal Fold Leukoplakiapubmed:28756936
- Label-Free Detection of Salivary Pepsin Using Gold Nanoparticle/Polypyrrole Nanocoral Modified Screen-Printed ElectrodePubmed:29882917
- Association between Pepsin in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid and Prognosis of Chronic Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease
- Pulmonary aspiration in preschool children with cystic fibrosisPubmed: 30558606
- Association of Bile Acid and Pepsin Micro-aspiration with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ExacerbationPubmed: 31423141
- Optimization of Saliva Collection and Immunochromatographic Detection of Salivary Pepsin for Point-of-Care Testing of Laryngopharyngeal RefluxPubmed: 31935973
- Presence of pepsin in laryngeal tissue and saliva in benign and malignant neoplasmsPubmed: 33103719
- Relationship Between Pepsin Expression and Dysplasia Grade in Patients With Vocal Cord LeukoplakiaPubmed: 32692278
- Association of pepsin and DNA damage in laryngopharyngeal reflux-related vocal fold polypsPubmed: 32889371
- The relationship between laryngopharyngeal reflux based on pepsin value and clinical characteristics of laryngeal cancer patients
- The Role of Salivary Pepsin in the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Evaluated Using High-Resolution Manometry and 24-Hour?¡33220027
- Pepsin properties, structure, and its accurate measurement: a narrative review
- The Impact of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux on Occurrence and Clinical Course of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis34338331
- Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) amylase and pepsin levels as potential biomarkers of aspiration pneumoniaPubmed:35715334
- Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation Improved the Quality of Life in Patients With Diarrhea-Irritable Bowel SyndromePubmed:35088760