Colitis
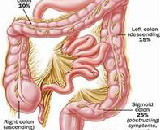
Colitis (pl. colitides) refers to an inflammation of the colon. Colitis may be acute and self-limited or chronic, i.e. persistent, and broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.In a medical context, the label colitis (without qualification) is used if: The cause of the inflammation in the colon is undetermined; for example, colitis may be applied to Crohn's disease at a time when the diagnosis is unknown, or The context is clear; for example, an individual with ulcerative colitis is talking about their disease with a physician who knows the diagnosis.
Models for Colitis are including models of ulcerative or chronic colitis induced by chemical drugs, such as acetic acid, dextran sulfate sodium(DSS), 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid(TNBS) and 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene etc.. A new ulcerative colitis model in rats by topical administration of sulfhydryl blockers. This model may be useful in studies on the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis and the evaluation of drugs for therapy.
Organism species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Disease model DSI515Mu01 Mouse Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Mu02 Mouse Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Mu03 Mouse Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Mu04 Mouse Model for Colitis In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Colitis (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Colitis (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Disease model DSI515Ra01 Rat Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Ra02 Rat Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Ra03 Rat Model for Colitis In Stock
- Tissue TSI515Ra19 Rat Tissue of Colitis In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Colitis (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Cavia (Guinea pig )
- Disease model DSI515Gu01 Cavia Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Gu02 Cavia Model for Colitis In Stock
- Disease model DSI515Gu03 Cavia Model for Colitis In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Colitis (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Colitis (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Disease model DSI515Rb01 Rabbit Model for Colitis In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Colitis (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Colitis (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Canis familiaris; Canine (Dog)
- Customized Service n/a Model for Colitis Disease Model Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Colitis (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Colitis (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer


