Mouse Model for Acute Lung Injury (ALI) 
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- UOM
- FOB US$ 200.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.DSI524Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsLPS induced Acute Lung Injury Model has a practical value in the research of drug screening and pathogenesis.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- Category
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- SourceLipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced
- Model Animal StrainsSPF Balb/c,4~6 weeks,body weight 20g~22g
- Modeling GroupingRandomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Test drug group (three doses)
- Modeling Period24hours
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Modeling Method
Model evaluation
1.Observation of lung injury:
Lung injury can be seen with the naked eye, large area of bleeding and exudation, can directly reflect the degree of lung injury.
2.Lung wet/dry weight ratio:
Lung wet/dry weight ratio is a direct indicator of pulmonary edema, and it is also a sensitive indicator of the severity of lung injury. After the occurrence acute lung injury (ALI), a large amount of fluid to the alveolar and interstitial fluid, leading to increased weight of the lungs, while the dry weight of the lung is not affected.
After killing the rats, cut trachea from whole lung and wet weight, dry the lung on 65℃ for 24hrs, and then calculate lung wet/ dry weight ratio.
Pathological results
Take the left lung 4% poly formaldehyde fixed, and then the normal lung tissue dehydration, paraffin embedded, sliced (thickness of 5μm), HE staining.
HE staining of lung tissue can directly response the degree of lung injury, ALI tissue pathology mainly in alveolar neutrophils and red blood cells exudation, alveolar wall transparent membrane formation. HE staining after can be in inflammatory cells was observed under low magnification infiltration, edema and injury.
At high magnification, the alveolar structure can be identified, and the degree of lung injury can be assessed and evaluated.
Scoring method: take 6 field of vision for bleeding and edema score.
0 points: no damage
1 points: <25% damage area
2 points: 25%~50% damage area
3 points: 50%~75% damage area
4 points: >75% damage area
Cytokines level
Anatomy of left lobectomy trachea, bronchial intubation, precooled sterile normal saline 1 ml, bronchoalveolar lavage 3 times, recycling bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) to a sterile centrifuge tube, 1500 R/min, 10 mins, collected and stored on 80℃, using ELISA kit for assay of TNF-a, IL-6, IL-1 beta and other cytokins in BALF.
Statistical analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison , P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
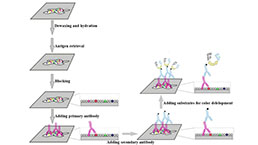 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
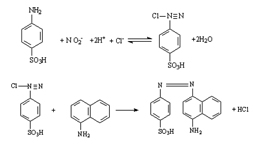 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
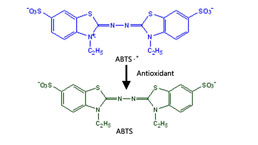 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
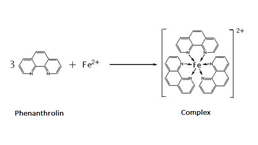 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits






