CLIA Kit for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) 
AKP; ALKP; Basic Phosphatase
- UOM
- FOB US$ 706.00 US$ 1,008.00 US$ 4,536.00 US$ 8,568.00 US$ 70,560.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SCB472Bo
- Organism SpeciesBos taurus; Bovine (Cattle) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsChemiluminescent immunoassay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseMetabolic pathwayTumor immunityInfection immunityHepatologyBone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
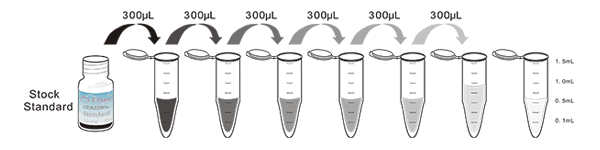
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 82-91 | 86 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-96 | 82 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 83-90 | 87 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 94-103% | 85-96% | 82-91% | 78-101% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 94-103% | 85-103% | 85-101% | 96-105% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-99% | 90-97% | 87-101% | 78-95% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Substrate A | 1×10mL | Substrate B | 1×2mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 100µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10 minutes at 37°C;
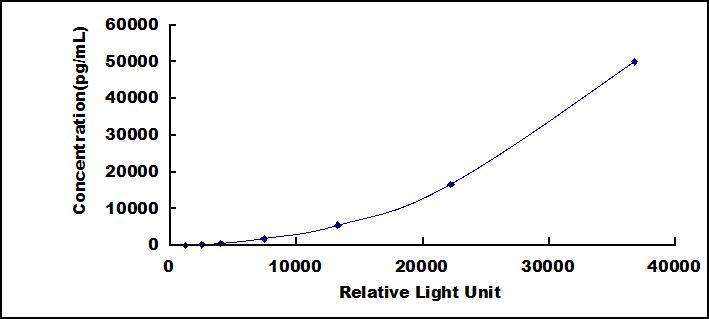
8. Read RLU value immediately.
Test principle
The microplate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microplate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. Then the mixture of substrate A and B is added to generate glow light emission kinetics. Upon plate development, the intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) level in the sample or standard.;
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Comparison of platelet rich fibrin and collagen as osteoblast-seeded scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applicationsWiley: source
- The role of atorvastatin in bone metabolism in male albino Wistar ratsIngenta: art00010
- Combined effect of strontium and zoledronate on hydroxyapatite structure and bone cell responsesScienceDirect: S0142961214003135
- Directing chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells with a solid-supported chitosan thermogel for cartilage tissue engineeringPubmed:24770944
- Strontium and zoledronate hydroxyapatites graded composite coatings for bone prosthesesPubmed:25706198
- The active role of osteoporosis in the interaction between osteoblasts and bone metastasesPubMed: 26057367
- Multi‐Layered Scaffolds for Osteochondral Tissue Engineering: In Vitro Response of Co‐Cultured Human Mesenchymal Stem CellsPubMed: 26126665
- Biological Evaluation of a Prototype Material made of Polyglycolic Acid and HydroxyapatiteArticle: Jhtb
- Antiresorption implant coatings based on calcium alendronate and octacalcium phosphate deposited by matrix assisted pulsed laser evaporationPubMed: 26445021
- On the Mechanism of Drug Release from Polysaccharide Hydrogels Cross-Linked with Magnetite Nanoparticles by Applying Alternating Magnetic Fields: the Case of DOXO Delivery2310-2861: 1
- Antioxidant and bone repair properties of quercetin-functionalized hydroxyapatite: an in vitro osteoblast-osteoclast-endothelial cell co-culture studyPubMed: 26689470
- A composite scaffold of MSC affinity peptide-modified demineralized bone matrix particles and chitosan hydrogel for cartilage regenerationPubMed: 26632447
- Antioxidant and bone repair properties of quercetin-functionalized hydroxyapatite: An in vitro osteoblast–osteoclast–endothelial cell co-culture studyPubmed:26689470
- Extracorporeal shock waves alone or combined with raloxifene promote bone formation and suppress resorption in ovariectomized rats.pubmed:28158228
- Adiponectin protects the rats liver against chronic intermittent hypoxia induced injury throughAMP-activated protein kinase pathway.pubmed:27678302
- An advanced tri-culture model to evaluate the dynamic interplay among osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and endothelial cells.pubmed:28240358
- Anti-osteoporotic effects of an antidepressant tianeptine on ovariectomized ratsS0753332216322752
- Biomimetic fabrication of antibacterial calcium phosphates mediated by polydopamine. pubmed:29049953
- Icaritin induces MC3T3-E1 subclone14 cell differentiation through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling activation.pubmed:28742995
- Peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor γ plays dual roles on experimental periodontitis in ratsPubmed:29574908
- Strontium‐Substituted Hydroxyapatite‐Gelatin Biomimetic Scaffolds Modulate Bone Cell ResponsePubmed:29877029
- Gradient coatings of strontium hydroxyapatite/zinc β-tricalcium phosphate as a tool to modulate osteoblast/osteoclast responsePubmed:29525694
- miRNA-133a-5p Inhibits the Expression of Osteoblast Differentiation-Associated Markers by Targeting the 3′ UTR ofPubmed:29359964
- The sole and combined effect of simvastatin and platelet rich fibrin as a filling material in induced bone defect in tibia of albino ratsPubmed: 30208342
- The decline of whole-body glucose metabolism in ovariectomized ratsPubmed: 30292771
- Hepatoprotective activity of Erythrina× neillii leaf extract and characterization of its phytoconstituentsPubmed: 28095910
- Multiple myeloma-derived exosomes are enriched of amphiregulin (AREG) and activate the epidermal growth factor pathway in the bone microenvironment …Pubmed: 30621731
- CoCr porous scaffolds manufactured via selective laser melting in orthopedics: Topographical, mechanical, and biological characterizationPubmed: 30689288
- Lead exposure inhibits osteoblastic differentiation and inactivates the canonical Wnt signal and recovery by icaritin in MC3T3-E1 subclone 14 cellsPubmed: 30731080
- Macrophage inhibits the osteogenesis of fibroblasts in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) wear particle-induced osteolysis
- Zn as the Factor of Alkaline Phosphatase in Periodontal Patients consuming Minangkabau food in West Sumatra, Indonesia
- AAV-anti-miR-214 prevents collapse of the femoral head in osteonecrosis by regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activitiesPubmed: 31739209
- Rutin Improves Bone Histomorphometric Values by Reduction of Osteoclastic Activity in Osteoporosis Mouse Model Induced by Bilateral OvariectomyPubmed: 32172552
- Effects of tricalcium silicate/sodium alginate/calcium sulfate hemihydrate composite cements on osteogenic performances in vitro and in vivoPubmed: 32138579
- Osteoprotective Activity and Metabolite Fingerprint via UPLC/MS and GC/MS of Lepidium sativum in Ovariectomized RatsPubmed: 32668691
- Matrilin-2 is a novel prognostic marker in osteosarcoma
- Research on the Mechanism of miR-142-5p's Promotion of the Function and Mineralization of Osteoblasts by Down-regulating the Expression of WWP1 Gene
- МАРКЕРЫ КОСТНОГО РЕМОДЕЛИРОВАНИЯ ПРИ ЗАМЕЩЕНИИ ДЕФЕКТАТРАБЕКУЛЯРНОЙ КОСТНОЙ ТКАНИ РЕЗОРБИРУЕМЫМИ И …
- Platinum nanoparticles supported on functionalized hydroxyapatite: Anti-oxidant properties and bone cells response
- Static Magnetic Field (2¨C4 T) Improves Bone Microstructure and Mechanical Properties by Coordinating Osteoblast/Osteoclast Differentiation in Mice33655538
- From hair to liver: emerging application of hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses liver cirrhosis by blocking the TGF-β/Smad signaling …Pubmed:35186473
- ECM1 modified HF-MSCs targeting HSC attenuate liver cirrhosis by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathwayPubmed:35136027
- Antiosteoporotic Nanohydroxyapatite Zoledronate Scaffold Seeded with Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Bone Regeneration: A 3D In Vitro ModelPubmed:35682677
- Effect of Antibacterial Enoxacin on the Properties of Injectable Nano-hydroxyapatite/Polyurethane Cement for Bone Repairing