CLIA Kit for Cathepsin K (CTSK) 
CTS-K; CTS02; CTSO; CTSO1; CTSO2; PKND; PYCD; Pycnodysostosis; Cathepsin O; Cathepsin X
- UOM
- FOB US$ 545.00 US$ 778.00 US$ 3,501.00 US$ 6,613.00 US$ 54,460.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SCA267Mu
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsChemiluminescent immunoassay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseInfection immunityBone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Cathepsin K (CTSK) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Cathepsin K (CTSK) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 80-105 | 86 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 86-101 | 96 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 82-92 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cathepsin K (CTSK) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cathepsin K (CTSK) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Cathepsin K (CTSK) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 92-105% | 87-101% | 81-99% | 98-105% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-93% | 79-89% | 89-103% | 80-98% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 83-101% | 79-97% | 90-98% | 89-101% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Substrate A | 1×10mL | Substrate B | 1×2mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 100µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10 minutes at 37°C;
8. Read RLU value immediately.
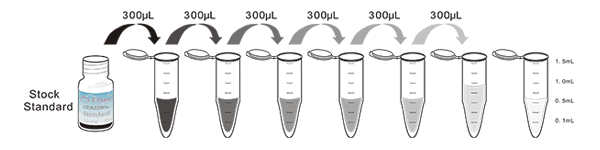
Test principle
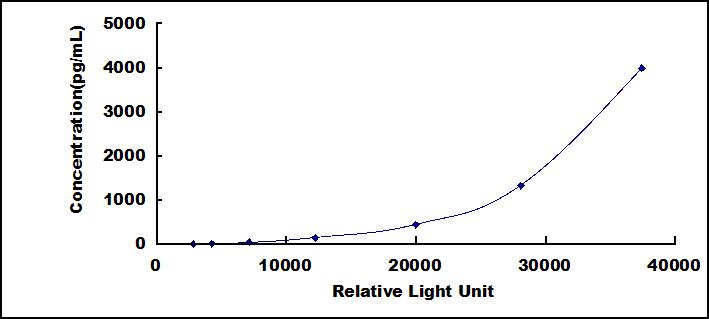
The microplate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Cathepsin K (CTSK). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microplate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to Cathepsin K (CTSK). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. Then the mixture of substrate A and B is added to generate glow light emission kinetics. Upon plate development, the intensity of the emitted light is proportional to the Cathepsin K (CTSK) level in the sample or standard.;
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 CLIA Kit Customized Service
CLIA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution
-
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Citations
- MRMT-1 rat breast carcinoma cells and models of bone metastases: improvement of an in vitro system to mimic the in vivo condition.PubMed: S0065128112000773
- Biochemical and clinical correlation of intraplaque neovascularization using contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the carotid arteryPubmed:24534452
- Drynaria total flavonoids decrease cathepsin K expression in ovariectomized ratsPubmed:25036175
- In vitro method for the screening and monitoring of estrogen-deficiency osteoporosis by targeting peripheral circulating monocytesPubMed: 26250906
- Cathepsin K Contributes to Cavitation and Collagen Turnover in Pulmonary TuberculosisPubMed: 26416658
- Effect of Vitamin D on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritispmc:PMC4822855
- TSC1 regulates osteoclast podosome organization and bone resorption through mTORC1 and Rac1/Cdc42Pubmed:29358671
- Comparative evaluation of cathepsin K levels in gingival crevicular fluid among smoking and nonsmoking patients with chronic periodontitisPubmed: 30409937
- A bioactive exopolysaccharide from marine bacteria Alteromonas sp. PRIM-28 and its role in cell proliferation and wound healing in vitroPubmed: 30851325
- Biomarkers of Compromised Implant Fixation
- Compound K induces neurogenesis of neural stem cells in thrombin induced nerve injury through LXRα signaling in micePubmed: 32371156
- Информационный алгоритм неинвазивной оценки остеорезорбтивного побочного действия глюкокортикостероидов у больных язвенным колитом
- Особенности остеоиммунологических аспектов остеорезорбции при периимплантите, хроническом пародонтите и раке альвеолярного отростка и …