ELISA Kit for Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) 
GNRH1; GRH; LNRH; LHRH; LH-RH I; Luliberin; Luteinizing-Hormone Releasing Hormone; Progonadoliberin-1; Gonadoliberin I; Gonadorelin; GnRH-associated peptide 1
- UOM
- FOB US$ 630.00 US$ 900.00 US$ 4,050.00 US$ 7,650.00 US$ 63,000.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.AEA843Po
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antibody Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEndocrinologyReproductive scienceNeuro scienceGenetic scienceHormone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 78-101 | 91 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 79-103% | 85-95% | 90-104% | 94-102% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
5. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
6. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

Test principle
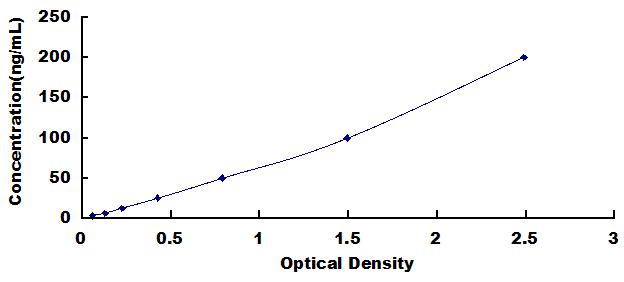
The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antigen. Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody. After TMB substrate solution is added, those wells that contain Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of Anti-Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Antibody (Anti-GnRH) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Maternal exposure to dioxin imprints sexual immaturity of the pups through fixing the status of the reduced expression of hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing …Pubmed:24132183
- Heavy Resistance Training and Supplementation With the Alleged Testosterone Booster Nmda has No Effect on Body Composition, Muscle Performance, and Serum Hormones Associated With the Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Resistance-Trained MalesPubmed:24570624
- Perfluorooctane sulfonate effects on the reproductive axis in adult male ratsPubmed:25171141
- Possible role of serotonin and neuropeptide Y on the disruption of the reproductive axis activity by perfluorooctane sulfonatePubmed:25623392
- Chronic exposure of female mice to an environmental level of perfluorooctane sulfonate suppresses estrogen synthesis through reduced histone H3K14 acetylation of the StAR promoter leading to deficits in follicular development and ovulationPubMed: 26358002
- Overexpression of PRL7D1 in Leydig Cells Causes Male Reproductive Dysfunction in MicePubmed:26771609
- OP0019-HPR Effectiveness of A Progressive Resistance Strength Program on Hand Osteoarthritis: A Randomised Controlled Trial60.1.abstract
- OP0021-HPR Sleep Disorders in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Relationship with Disease Activity60.3.abstract
- Exposure of pregnant mice to perfluorobutanesulfonate causes hypothyroxinemia and developmental abnormalities in female offspringpubmed:27803384
- OP0020 The Association of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone and Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritiscontent:75
- Pyrethroid Insecticide Cypermethrin Accelerates Pubertal Onset in Male Mice via Disrupting Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axispubmed:28731686
- Impact of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate on Reproductive Ability of Female Mice through Suppression of Estrogen Receptor a-Activated Kisspeptin Neurons10.1093:toxsci
- Nectin-like molecule 2, a necessary sexual maturation regulator, participates in congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadismPubmed: 32535046
- Pathophysiological Changes in Female Rats with Estrous Cycle Disorder Induced by Long-Term Heat StressPubmed: 32685488
- Zihuai recipe alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced diminished ovarian reserve via suppressing PI3K/AKT-mediated apoptosis33422655
- Zika virus infection in the ovary induces continuously elevated progesterone level and compromises conception in interferon α/β receptor-deficient mice34730391