ELISA Kit for Cathepsin D (CTSD) 
CPSD; CLN10; Lysosomal Aspartyl Protease; Ceroid-Lipofuscinosis,Neuronal 10
- UOM
- FOB US$ 559.00 US$ 798.00 US$ 3,591.00 US$ 6,783.00 US$ 55,860.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.CEB280Bo
- Organism SpeciesBos taurus; Bovine (Cattle) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunity
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Cathepsin D (CTSD) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Cathepsin D (CTSD) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 78-90 | 81 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 78-93 | 83 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-104 | 81 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cathepsin D (CTSD) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cathepsin D (CTSD) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Cathepsin D (CTSD) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 78-97% | 90-98% | 95-102% | 78-96% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-101% | 88-96% | 92-101% | 96-104% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 89-98% | 96-104% | 89-98% | 78-94% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
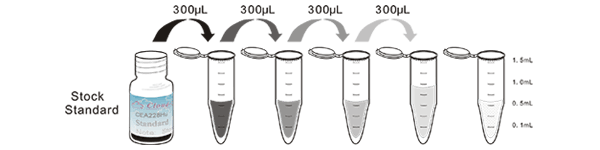
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
Test principle
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. A monoclonal antibody specific to Cathepsin D (CTSD) has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled Cathepsin D (CTSD) and unlabeled Cathepsin D (CTSD) (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to Cathepsin D (CTSD). After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of Cathepsin D (CTSD) in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of Cathepsin D (CTSD) in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Cathepsin D is released after severe tissue trauma in vivo and is capable of generating C5a in vitroScienceDirect: S0161589011008297
- Plasma Cathepsin D Levels: A Novel Tool to Predict Pediatric Hepatic InflammationPubMed: 25732418
- Plasma cathepsin D correlates with histological classifications of fatty liver disease in adults and responds to interventionpubmed:27922112
- Berberine ameliorates intrahippocampal kainate-induced status epilepticus and consequent epileptogenic process in the rat: Underlying mechanismspubmed:28061403
- Limited applicability of cathepsin D for the diagnosis and monitoring of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis
- Plasma cathepsin D activity is negatively associated with hepatic insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese humansPubmed: 31690989
- Iron and Advanced Glycation End Products: Emerging Role of Iron in Androgen Deficiency in ObesityPubmed: 32235809
- LVV-hemorphin-7 (LVV-H7) plays a role in antinociception in a rat model of alcohol-induced pain disorders33253777
- Identification of Cathepsin D as a Plasma Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease33445607
- Analysis of silymarin-modulating effects against acrylamide-induced cerebellar damage in male rats: Biochemical and pathological markers33965515
- PGRS Domain of Rv0297 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is Involved in Modulation of Macrophage Functions to Favor Bacterial Persistence33042856
- Serum CathepsinD in pregnancy: relation with metabolic and inflammatory markers and effects of fish oils and probioticsPubmed:35304048
- A Comparison of Various Chips Used for the Manufacture of Biosensors Applied in Non-Fluidic Array SPRi, Based on the Example of Determination of Cathepsin DPubmed:35049649