ELISA Kit for Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) 
B-FGF; BFGF; FGFB; HBGH-2; Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor; Heparin-binding growth factor 2
- UOM
- FOB US$ 529.00 US$ 756.00 US$ 3,402.00 US$ 6,426.00 US$ 52,920.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.CEA551Po
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryCytokineTumor immunityInfection immunity
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 96-103 | 101 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 92-101 | 96 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 95-105 | 101 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, Basic (FGF2) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 95-102% | 98-105% | 86-101% | 94-102% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 88-97% | 92-99% | 83-94% | 95-102% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 80-92% | 82-96% | 99-105% | 90-99% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
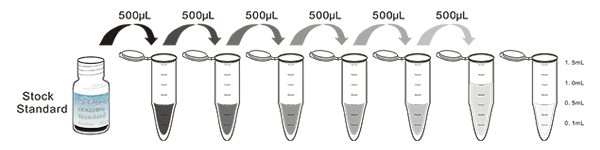
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
Test principle
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. An antibody specific to FGF2 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled FGF2 and unlabeled FGF2 (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to FGF2. After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of FGF2 in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of FGF2 in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- The influence of nutrients, biliary-pancreatic secretions, and systemic trophic hormones on intestinal adaptation in a Roux-en-Y bypass modelPubMed: 20438940
- Effect of heparan sulfate and gold nanoparticles on muscle development during embryogenesisPubMed: PMC3254262
- Effect of taurine and gold nanoparticles on the morphological and molecular characteristics of muscle development during chicken embryogenesisTandfonline: 644918
- Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) Enhances Engraftment and Angiogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Diabetic Hindlimb IschemiaPubmed: 22266669
- Electrospun Fibers with Plasmid bFGF Polyplex Loadings Promote Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic RatsPubmed: 22091745
- Antiangiogenic Activities of Cinnamon, Black and Green Tea Extracts on Experimentally Induced Breast Cancer in RatsScialert: Source
- Silver nanoparticles administered to chicken affect VEGFA and FGF2 gene expression in breast muscle and heart.PubMed: 22827927
- Carbon nanoparticles downregulate expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in the heart during embryogenesisPubMed: PMC3771850
- Nano-Nutrition of Chicken Embryos. The Effect of in Ovo Administration of Diamond Nanoparticles and L-Glutamine on Molecular Responses in Chicken Embryo Pectoral MusclesNCBI:PMC3856104
- Nano-nutrition of chicken embryos. The effect of silver nanoparticles and ATP on expression of chosen genes involved in myogenesisPubmed: 23952606
- Role of sensory and motor intensity of electrical stimulation on fibroblastic growth factor-2 expression, inflammation, vascularization, and mechanical strength of full-thickness woundsPubmed: 23934870
- Carboxypeptidase E-ΔN, a Neuroprotein Transiently Expressed during Development Protects Embryonic Neurons against Glutamate NeurotoxicityPubmed:25426952
- Effects of Hemostatic Agents on Fibroblast CellsLww:Source
- bFGF-grafted electrospun fibrous scaffolds via poly(dopamine) for skin wound healingRsc:Source
- Effect of silver nanoparticles and hydroxyproline, administered in ovo, on the development of blood vessels and cartilage collagen structure in chicken embryosPubmed:25530495
- The effects of self-assembling peptide RADA16 hydrogel on malignant phenotype of human hepatocellular carcinoma cellPubMed: 26628972
- Evaluation of Changes in Doppler Ultrasonography Indices and Levels of Maternal Serum Angiogenic Factors throughout Pregnancy in EwesScience: Article
- Hypoxia-induced secretion of IL-10 from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell promotes growth and cancer stem cell properties of Burkitt lymphomaPubMed: 26695151
- Preparation and characterization of pro-angiogenic gel derived from small intestinal submucosaarticle:S1742706115301410
- Surface biofunctional drug-loaded electrospun fibrous scaffolds for comprehensive repairing hypertrophic scarsPubmed:26774564
- Changes in growth factor levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of autism patients after transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cellsPubmed:27323064
- 3-O-Methyldopa inhibits astrocyte-mediated dopaminergic neuroprotective effects of l-DOPApubmed:27456338
- 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid-Based Photodynamic Therapy Restrains Pathological Hyperplasia of Fibroblasts898221
- FGF-2-mediated FGFR1 signaling in human microvascular endothelial cells is activated by vaccarin to promote angiogenesispubmed:28841454
- 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid-Based Photodynamic Therapy Restrains Pathological Hyperplasia of Fibroblastspubmed:28052053
- Platelet-derived growth factor and stromal cell-derived factor-1 promote the skin wound repairing effect of bone mesenchymal stem cells: a key role of matrix metalloproteinase 1 and collagensISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058424
- The Combination of Acellular Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa (SIS) Cryogel Granules and Adipose Tissue Improves the Survival Ratio of Fat Grafting in Mice10.1166/jbt.2017.1652
- Lower Senescence of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells than Donor-Matched Bone Marrow Stem Cells for Surgical Ventricular RestorationPubmed:29630447
- Increased serum FGF2 levels in first-episode, drug-free patients with schizophreniaPubmed: 30172685
- Silencing of Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cellsPubmed: 30359541
- Gene-activating skin substitute comprised of PLLA/POSS nanofibers and plasmid DNAs encoding ANG and bFGF promotes in vivo revascularization and …
- HOXA9 is a novel myopia risk genePubmed: 30674274
- Immunomodulated electrospun fibrous scaffolds via bFGF camouflage for pelvic regeneration
- A novel xeno-free culture system for human retinal pigment epithelium cellsPubmed: 31024807
- Low Degree Hyaluronic Acid Crosslinking Inducing the Release of TGF-Β1 in Conditioned Medium of Wharton's Jelly-Derived Stem Cells
- Bisphenol S triggers the malignancy of hemangioma cells via regulation of basic fibroblast growth factorPubmed: 31669319
- β-Galactosylceramidase Deficiency Causes Bone Marrow Vascular Defects in an Animal Model of Krabbe DiseasePubmed: 31905906
- Long non‑coding RNA NORAD regulates angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via miR‑590‑3p under hypoxic conditionsPubmed: 32323787
- Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor is Involved in Bisphenol S Induced Proliferation of Hemangioma Cells
- New design to remove leukocytes from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) based on cell dimension rather than density33842739
- Highly interconnected inverse opal extracellular matrix scaffolds enhance stem cell therapy in limb ischemia33878473
- Double Layer Composite Membrane for Preventing Tendon Adhesion and Promoting Tendon Healing33812576
- Ratlarda deneysel kolon anastomoz ka?a?? modelindeintraperitoneal atorvastatin uygulamas?n?n anastomozka?a?? onar?m? ¨¹zerine etkisi
- Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 and fibroblast growth factor 21 in alcohol-induced liver cirrhosisPubmed:35070009
- Human adipose-derived stem cell-loaded small intestinal submucosa as a bioactive wound dressing for the treatment of diabetic wounds in rats