ELISA Kit for Cholecystokinin (CCK) 
CCK-PZ
- UOM
- FOB US$ 441.00 US$ 630.00 US$ 2,835.00 US$ 5,355.00 US$ 44,100.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.CEA802Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunityEndocrinologyNeuro scienceHepatologyHormone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Cholecystokinin (CCK) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Cholecystokinin (CCK) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 82-92 | 88 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 94-101 | 98 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 95-105 | 101 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cholecystokinin (CCK) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cholecystokinin (CCK) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Cholecystokinin (CCK) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 90-105% | 78-99% | 98-105% | 81-91% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 88-97% | 94-102% | 96-105% | 86-94% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 93-102% | 78-96% | 97-104% | 86-101% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
Test principle
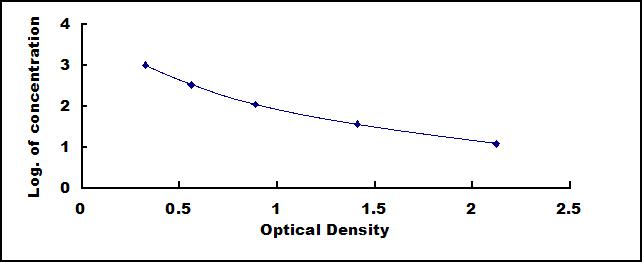
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. An antibody specific to cholecystokinin has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled cholecystokinin and unlabeled cholecystokinin (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to cholecystokinin. After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of cholecystokinin in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of cholecystokinin in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Disturbed release of cholecystokinin in pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarumPubmed:25331205
- Effects of sphincter of Oddi motility on the formation of cholesterol gallstonesPubmed:27350732
- Luhong formula inhibits myocardial fibrosis in a paracrine manner by activating thegp130/JAK2/STAT3 pathway in cardiomyocytes.pubmed:28115285
- Cholecystokinin Expression in the Development of Postinfarction Heart Failure.pubmed:29130944
- Assessment of the role of cholecystokinin in hyperemesis gravidarum and correlation with its severity:
- Effects of dietary leucine and phenylalanine on pancreas development, enzyme activity, and relative gene expression in milk-fed Holstein dairy calvesPubmed:29477524
- Alignments of endocrine, anthropometric, and metabolic parameters in type 2 diabetes after intervention with an Okinawa-based Nordic dietPubmed:29599686
- The Relationship of Appetite-Regulating Hormones in the Development of Cardiac CachexiaPubmed: 30799377
- Hejie Zhitong prescription promotes sleep and inhibits nociceptive transmission-associated neurotransmitter activity in a rodent migraine modelPubmed: 33014123
- Appetite and Satiety Effects of the Acute and Regular Consumption of Green Coffee Phenols and Green Coffee Phenol/Oat β-Glucan Nutraceuticals in Subjects with …34828792
- The microbiota-gut-kidney axis mediates host osmoregulation in a small desert mammalPubmed:35379849
- Digestion characteristics of quinoa, barley and mungbean proteins and the effects of their simulated gastrointestinal digests on CCK secretion in enteroendocrine STC …Pubmed:35587126