ELISA Kit for Immunoglobulin E (IgE) 
IGHE; Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Epsilon; Ig epsilon chain C region
- UOM
- FOB US$ 479.00 US$ 684.00 US$ 3,078.00 US$ 5,814.00 US$ 47,880.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.CEA545Rb
- Organism SpeciesOryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryInfection immunityImmune moleculeHematologyAutoimmunity
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 86-93 | 90 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 96-104 | 99 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 88-96 | 92 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Immunoglobulin E (IgE) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Immunoglobulin E (IgE) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
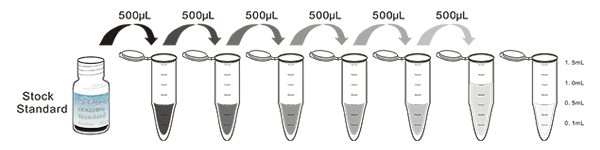
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 85-94% | 87-99% | 96-105% | 82-91% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 88-99% | 93-101% | 90-97% | 89-97% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 96-105% | 98-105% | 87-103% | 85-92% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
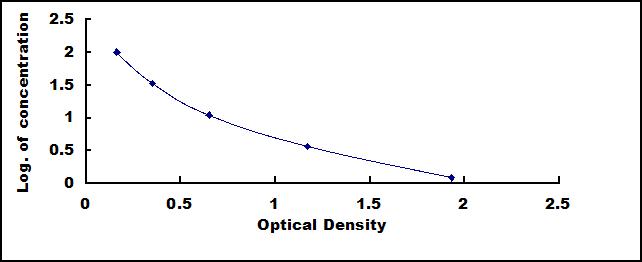
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
Test principle
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. A monoclonal antibody specific to Immunoglobulin E (IgE) has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and unlabeled Immunoglobulin E (IgE) (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to Immunoglobulin E (IgE). After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- IL17A gene polymorphisms, serum IL-17A and IgE levels, and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infectionPubMed: 23280722
- IL21 and IL21R polymorphisms and their interactive effects on serum IL-21 and IgE levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infectionPubMed: 23354321
- Passive transfer of tumour-derived MDSCs inhibits asthma-related airway inflammationPubmed: 24313384
- Topical Lyogel Containing Corticosteroid Decreases IgE Expression and Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy Against Atopic EczemaPubMed: 25511806
- Reduced airway microbiota diversity is associated with elevated allergic respiratory inflammationPubMed: 26123423
- The protective role of vitamin D3 in a murine model of asthma via the suppression of TGF-β/Smad signaling and activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.pubmed:27484042
- Oral administration of Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313‐1 reduces ovalbumin‐induced allergic airway inflammation in micepubmed:28250847
- Catalpol alleviates ovalbumin-induced asthma in mice: Reduced eosinophil infiltration in the lungpubmed:27992791
- Oral administration of Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313-1 reduces ovalbumin-induced allergic airway inflammation in micepubmed:28122397
- Protective effects of astragaloside IV against ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis are mediated by T-box protein expressed in T cells/GATA-3 and forkhead box protein 3/retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt.pubmed:28586019
- Commensal bacteria aggravate allergic asthma via NLRP3/IL-1β signaling in post-weaning mice10.1016:j.jaut.2018.07.003
- Sub-chronic inhalation of reclaimed water-induced fibrotic lesion in a mouse modelPubmed:29655095
- Investigation of hypersensitivity potential of diacetyl by determining cytokine profilesPubmed:29233007
- Changes in Th1/Th2-producing cytokines during acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary diseasePubmed:29950127
- Effects of catalpol on bronchial asthma and its relationship with cytokinesPubmed: 30536454
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Modulates the Immune Response of Allergic Rhinitis in a Rat ModelPubmed: 30781605
- Metabolomics analysis of baicalin on ovalbumin-sensitized allergic rhinitis rats
- Antiallergical Effect of New Combined Nazal Aerodisperse System in the Conditions of Experimental Allergic Rhinitis
- Inhibitory effects of catalpol coordinated with budesonide and their relationship with cytokines and Interleukin-13 expressionPubmed: 31737193
- Animal models for analysis of hypersensitivity reactions to Shuanghuanglian injectionPubmed: 32302806
- Protective effect of Asarum sieboldii essential oil on ovalbumin induced allergic rhinitis in ratPubmed: 32395767
- Synergistic Phage-surfactant Combination Clears IgE-promoted Staphylococcus aureus Aggregation in Vitro and Enhances the Effect in VivoPubmed: 32335278
- Aggravation of Airway Inflammation in RSV-Infected Asthmatic Mice Following Infection-Induced Alteration of Gut Microbiota
- Tissue-Engineered Decellularized Allografts for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
- Biomarkers of Allergic Asthma and their Association with Serum Parameters
- Qingfei oral liquid inhibited autophagy to alleviate inflammation via mTOR signaling pathway in RSV-infected asthmatic mice33706133
- Trace endotoxin in reclaimed water is only one of the risk sources in subchronic inhalation exposure34090073
- Effectiveness of biomarkers and serum parameters in determination allergic asthma and detection of its severity
- Roles Played by the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α Pathway and IL-17A in the Chinese Subtype of Chronic Sinusitis with Nasal PolypsPubmed:35075349
- Dapagliflozin mitigates ovalbumin-prompted airway inflammatory-oxidative successions and associated bronchospasm in a rat model of allergic asthmaPubmed:35549595