ELISA Kit for P-Selectin (SELP) 
CD62P; Selectin, Platelet; PSEL; GMP140; LECAM3; GRMP; GMRP; PADGEM; Leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion molecule 3; Platelet activation dependent granule-external membrane
- UOM
- FOB US$ 426.00 US$ 608.00 US$ 2,736.00 US$ 5,168.00 US$ 42,560.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.SEA569Ra
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryCD & Adhesion moleculeTumor immunityInfection immunity
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant P-Selectin (SELP) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of P-Selectin (SELP) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 90-104 | 99 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 84-95 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level P-Selectin (SELP) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level P-Selectin (SELP) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of P-Selectin (SELP) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 89-102% | 94-102% | 85-97% | 87-94% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 81-101% | 88-96% | 82-98% | 95-102% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

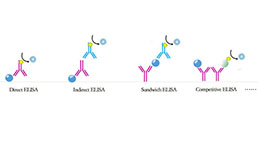
Test principle
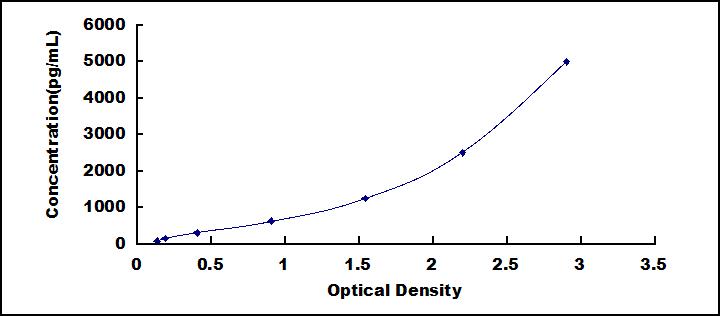
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to P-Selectin (SELP). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to P-Selectin (SELP). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain P-Selectin (SELP), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of P-Selectin (SELP) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution
-
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Citations
- Effect of Hirulog-Like Peptide on Balloon Catheter Injury-Induced Neointimal Formation in Femoral Arteries of Minipigs and Relationship with Inflammatory MediatorsKarger: 000257340
- Secretome of apoptotic peripheral blood cells (APOSEC) attenuates microvascular obstruction in a porcine closed chest reperfused acute myocardial infarction model: role of platelet aggregation and vasodilationPubMed: 22899170
- Endothelial gene expression and molecular changes in response to radiosurgery in in vitro and in vivo models of cerebral arteriovenous malformationsPubmed: 24199192
- Involvement of nitric oxide with activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitisPubmed:24992835
- MRI-compatible Nb–60Ta–2Zr alloy used for vascular stents: Haemocompatibility and its correlation with protein adsorptionPubmed:25063132
- Chemical sympathectomy attenuates inflammation, glycocalyx shedding and coagulation disorders in rats with acute traumatic coagulopathy.Pubmed:25325345
- Systemic and Flap Inflammatory Response Associates with Thrombosis in Flap Venous CrisisPubmed:25448261
- Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on advanced glycation endproduct-induced aortic endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: possible roles of Rho kinase- and AMP kinase-mediated nuclear factor κB signaling pathwaysPubmed:26758998
- Protective effects of sinomenine against LPS-induced inflammation in piglets.pubmed:28757275
- L-Carnitine Supplementation Increases Trimethylamine-N-Oxide but not Markers of Atherosclerosis in Healthy Aged WomenPubmed: 30485835
- Evaluating the Platelet Activation Related to the Degradation of Biomaterials by Scheme of Molecular Markers
- Molecular mechanisms of lead-induced changes of selenium status in mice livers through interacting with selenoprotein P
- Feasibility study of use of rabbit blood to evaluate platelet activation by medical devicesPubmed: 31838449
- Polycaprolactone vascular graft with epigallocatechin gallate embedded sandwiched layer-by-layer functionalization for enhanced antithrombogenicity and anti …Pubmed: 31982435
- The Inhibition of P-Selectin Reduced Severe Acute Lung Injury in Immunocompromised MicePubmed: 32377309
- The binding of autotaxin to integrins mediates hyperhomocysteinemia-potentiated platelet activation and thrombosis34559203
- The effect of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine on arterial thrombosis development and platelet aggregation in female ratsPubmed:35183388
- The inhibition of TRIM35-mediated TIGAR ubiquitination enhances mitochondrial fusion and alleviates renal ischemia-reperfusion injuryPubmed:35421414
- Construction of a rabbit model with vinorelbine administration via peripherally inserted central catheter and dynamic monitoring of changes in phlebitis and thrombosisPubmed:35126715