ELISA Kit for Vitamin C (VC) 
AA; L-Ascorbic Acid; Ascorbate
- UOM
- FOB US$ 557.00 US$ 796.00 US$ 3,580.00 US$ 6,763.00 US$ 55,692.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.CEA913Ge
- Organism SpeciesPan-species (General) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayInfection immunityNutrition metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Vitamin C (VC) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Vitamin C (VC) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 89-99 | 95 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 99-105 | 102 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-94 | 84 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Vitamin C (VC) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Vitamin C (VC) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
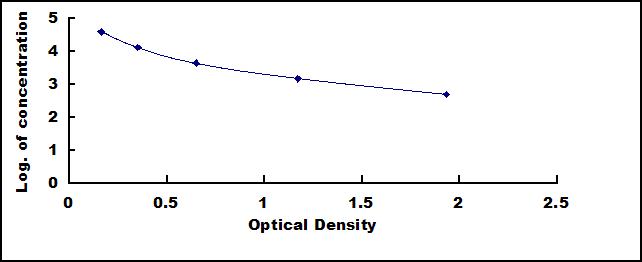
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Vitamin C (VC) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 84-105% | 94-103% | 79-99% | 78-97% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 85-97% | 80-99% | 80-94% | 89-103% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 88-96% | 96-104% | 78-89% | 79-93% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
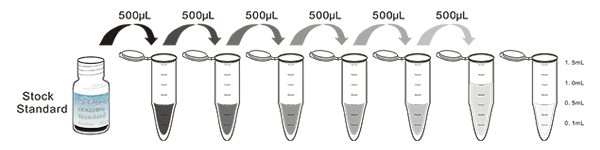
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
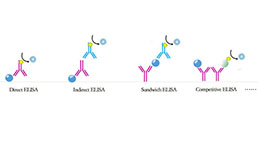
Test principle
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. An antibody specific to VC has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled VC and unlabeled VC (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to VC. After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of VC in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of VC in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Salivary 1, 5-Anhydroglucitol and Vitamin Levels in Relation to Caries Risk in Children
- Vitamin A, C, D, E and B12 Levels in Leprosy: A Case Control Study
- Vitamin C¡ªSources, Physiological Role, Kinetics, Deficiency, Use, Toxicity, and Determination33668681