High Sensitive ELISA Kit for Collagen Type IV (COL4) 
Type-IV Collagen
- UOM
- FOB US$ 485.00 US$ 693.00 US$ 3,119.00 US$ 5,891.00 US$ 48,510.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.HEA180Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunityHepatology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 93-101 | 97 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 81-90 | 86 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 81-101 | 87 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 86-98% | 87-102% | 91-99% | 84-104% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 79-94% | 87-103% | 84-96% | 78-91% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-91% | 85-103% | 86-94% | 88-96% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

Test principle
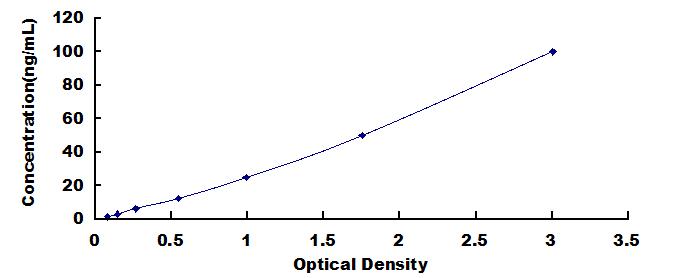
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of High Sensitive Collagen Type IV (COL4) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Overexpression Remarkably Ameliorated Glomerular Injury in a Rat Model of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Comparison with ACE InhibitionMolMed: 10_11_liu
- Advanced oxidation protein products induce mesangial cell perturbation through PKC-dependent activation of NADPH oxidasePubMed: 19019916
- Serum Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 as a Marker of Intimal HyperplasiaScienceDirect: S0022480409001942
- Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jellyPubmed: 24739658
- Identification of compounds from the water soluble extract of Cinnamomum cassia barks and their inhibitory effects against high-glucose-induced mesangial cells.Pubmed: 24013407
- Bioactive compounds from Cornus officinalis fruits and their effects on diabetic nephropathyScienceDirect: S0378874114002414
- Protective Effects of Norursodeoxycholic Acid Versus Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Thioacetamide-induced Rat Liver FibrosisScienceDirect: S0973688314000073
- Attenuation of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by a?aí extract preconditioning in a rat modelPubmed:25476829
- Mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation, gene expression and protein production in human platelet-rich plasma-supplemented mediaPubmed:Pmc4130592
- Trophoblasts and Decidual Stromal Cells Regulate Decidual NK Cell Functions Via Interaction between Collagen and LAIR-1Pubmed:24548186
- Camel milk attenuates the biochemical and morphological features of diabetic nephropathy: Inhibition of Smad1 and collagen type IV synthesisPubMed: 25617480
- The Relationship of the Degree of Hepatic Fibrosis with Hyaluronic Acid, Type 4 Collagen, and Procollagen Type 3 N-Terminal Peptide Levels in Patients with Chronic Viral HepatitisOpenview: 8A0B8C97D72C61741371F33508760B75
- Pathological characterization and morphometric analysis of hepatic lesions in SHRSP5/Dmcr, an experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model, induced by high-fat and high-cholesterol dietdoi:10.1111
- Clinical significance of serum laminin and typeâIV collagen levels in cutaneous melanoma patientsPubmed:27330797
- Key Matrix Proteins Within the Pancreatic Islet Basement Membrane Are Differentially Digested During Human Islet Isolation.pubmed:27456745
- Human decidua mesenchymal stem cells regulate decidual natural killer cell function via interactions between collagen and leukocyte‑associated immunoglobulin‑like receptor 110.3892:mmr.2017.6921
- Phase I and biomarker study of plerixafor and bevacizumab in recurrent high-grade gliomaPubmed:29941486
- Adenovirus‑mediated knockdown of activin A receptor type 2A attenuates immune‑induced hepatic fibrosis in mice and inhibits interleukin‑17‑induced …Pubmed:29620144
- Corn silk (Zea mays L.), a source of natural antioxidants with α-amylase, α-glucosidase, advanced glycation and diabetic nephropathy inhibitory activitiesPubmed: 30530231
- High amplitude stretching of ATII cells and fibroblasts results in profibrotic effectsPubmed: 31290711
- Growth hormone induces Notch1 signaling in podocytes and contributes to proteinuria in diabetic nephropathyPubmed: 31511328
- Pantoea agglomerans chronic exposure induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lung epithelial cells and mice lungsPubmed: 32146192
- Beneficial impact of cathelicidin on hypersensitivity pneumonitis treatment¡ªIn vivo studies33999928
- Advanced glycation end-products associate with podocytopathy in type II diabetic patients
- Increase in Serum MMP-9 and TIMP-1 Concentrations during Alcohol Intoxication in Adolescents—A Preliminary StudyPubmed:35625637