High Sensitive ELISA Kit for Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) 
FABPI; IFABP; I-FABP; Intestinal-type fatty acid-binding protein
- UOM
- FOB US$ 384.00 US$ 548.00 US$ 2,466.00 US$ 4,658.00 US$ 38,360.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.HEA559Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayTumor immunityEndocrinologyCardiovascular biology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 94-101 | 97 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 97-105 | 102 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 87-94 | 90 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 97-105% | 80-101% | 78-104% | 79-90% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 90-102% | 93-101% | 78-95% | 81-94% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 82-103% | 78-104% | 78-88% | 81-93% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

Test principle
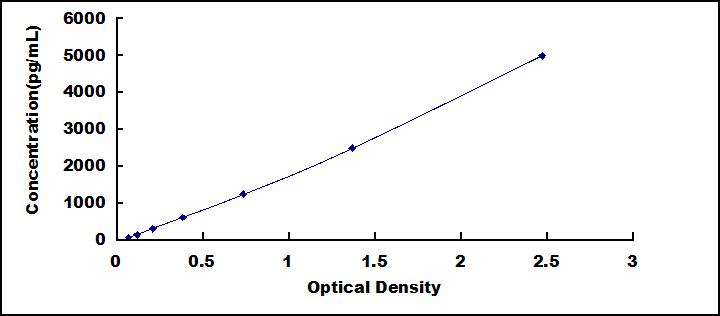
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of High Sensitive Fatty Acid Binding Protein 2, Intestinal (FABP2) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit lipid metabolism and modulate leptin and adiponectin secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytesPubMed: 25952883
- Elevation of HO-1 Expression Mitigates Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Restores Tight Junction Function in a Rat Liver Transplantation ModelPubMed: 26064429
- Immunomodulatory potential of β-glucan as supportive treatment in porcine rotavirus enteritis.pubmed:28895864
- Protective effect of aplysin on liver tissue and the gut microbiota in alcohol-fed ratspubmed:28622357
- Effect of Porcine Rotavirus Enteritis on Concentrations of Interferonγ, Immunoglobulin-G and Intestinal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein-2 and Peripheral Leukocyte Function10.5958/0973-9149.2017.00011.9
- Activated Α7nachr Improves Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and Intestinal Injury Induced by Cardiopulmonary Bypass in Rats: Inhibition of the Proinflammatory …Pubmed:29672286
- Lack of liver steatosis in germ-free mice following hypercaloric dietsPubmed:29926176
- Protective Effect of Aplysin Supplementation on Intestinal Permeability and Microbiota in Rats Treated with Ethanol and IronPubmed:29861488
- Intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) as a marker for acute intestinal ischemiaDoi: 10.18203/2349-2902.isj20190058
- Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Cognitive Function and Risk of Falls in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Randomized Trial
- Immunomodulating dose of levamisole stimulates innate immune response and prevents intestinal damage in porcine rotavirus diarrhea: a restricted-randomized …Pubmed: 30790158
- Role of Aquaporin-3 in Intestinal Injury Induced by SepsisPubmed: 31582652
- FABP1 and FABP2 as markers of diabetic nephropathyPubmed: 32922200
- Hydrogen attenuates radiation-induced intestinal damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory responsePubmed: 32361189
- Markers of Intestinal Damage in Individuals with and without Obesity during a 12-Week Exercise Period.
- Effects of fucoidan on tumor prevention and gut flora
- Effect of Lactobacillus casei on lipid metabolism and intestinal microflora in patients with alcoholic liver injury33514869
- The ¦Á2AR/Caveolin©\1/p38MAPK/NF©\¦ÊB axis explains dexmedetomidine protection against lung injury following intestinal ischaemia©\reperfusion34114328
- Somatization in patients with predominant diarrhoea irritable bowel syndrome: the role of the intestinal barrier function and integrity34022802
- Impact of Successive Exertional Heat Injuries on Thermoregulatory and Systemic Inflammatory Responses in Mice34528459
- The protective effects of HIF-1α activation on sepsis induced intestinal mucosal barrier injury in rats model of sepsisPubmed:35576220