High Sensitive ELISA Kit for Osteopontin (OPN) 
SPP1; BNSP; BSPI; ETA1; Secreted Phosphoprotein 1; Bone Sialoprotein I; Early T-Lymphocyte Activation 1; Nephropontin; Urinary stone protein; Uropontin
- UOM
- FOB US$ 554.00 US$ 792.00 US$ 3,564.00 US$ 6,732.00 US$ 55,440.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.HEA899Ca
- Organism SpeciesCanis familiaris; Canine (Dog) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunityBone metabolism
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 80-104 | 97 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 93-101 | 97 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 95-102 | 99 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 82-99% | 97-105% | 98-105% | 80-92% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 89-96% | 82-101% | 99-105% | 86-101% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 95-103% | 92-101% | 83-93% | 96-104% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

Test principle
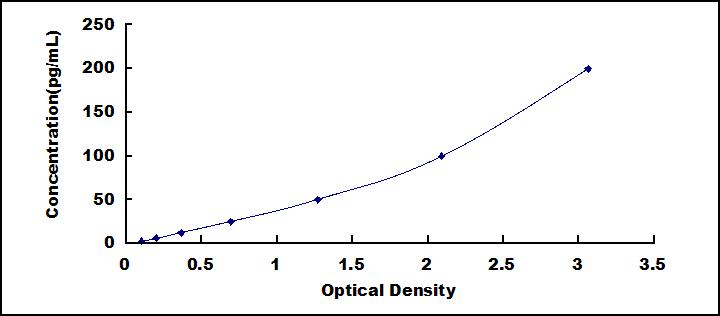
The test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody specific to High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN). Next, Avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. After TMB substrate solution is added, only those wells that contain High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN), biotin-conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of High Sensitive Osteopontin (OPN) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Proliferation and osteogenesis of immortalized bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in porous polylactic glycolic acid scaffolds under perfusion culturePubMed: 19280635
- Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patientsPubMed: 19747583
- Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin levels in synovial fluid correlate with disease severity of knee osteoarthritis.Jrheum: source
- Suppression of tumor growth in xenograft model mice by small interfering RNA targeting osteopontin delivery using biocompatible poly(amino ester)ScienceDirect: S0378517312003742
- The use of non-viral gene vectors for bioactive poly-(D, L-lactide) implant surfaces in bone tissue engineeringEcmjournal: Source
- Influence of Seminal Plasma Antioxidants and Osteopontin on Fertility of the Arabian HorseScienceDirect: Source
- Treatment with Carnitine Enhances Bone Fracture Healing under Osteoporotic and/or Inflammatory ConditionsWiley:Source
- Tension Force-Induced ATP Promotes Osteogenesis Through P2X7 Receptor in OsteoblastsPubmed:24905552
- Treatment with α-lipoic acid enhances the bone healing after femoral fracture model of ratsPubmed:25038619
- The interplay among iron metabolism, endothelium and inflammatory cascade in dysmetabolic disordersPubmed:25245337
- Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-induced ATP increases bone formation via the P2X7 receptor in osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cellsPubmed:25542352
- Effects of magnesium degradation products on mesenchymal stem cell fate and osteoblastogenesisPubMed: 26283150
- An Attempt to Evaluate Selected Aspects of “Bone–Fat Axis” Function in Healthy Individuals and Patients With Pancreatic CancerPubMed: 26266370
- Osteogenic Differentiation of Canine Adipose Stem Cells Cultured in Alginate-Fibrin-Based HydrogelContent: Asp
- Osteopontin level correlates negatively with tumor shrinkage in neoadjuvant chemoradiation of locally advanced rectal cancerIndex.Php: Amor
- Defective Initiation of Liver Regeneration in Osteopontin-Deficient Mice after Partial Hepatectomy due to Insufficient Activation of IL-6/Stat3 PathwayPubMed: 26327817
- Perioperative Clinical Investigation of Serum VEGF, CA19-9 and OPN Levels in Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma.Ebscohost
- Serum Osteopontin as a Novel Biomarker for Muscle Regeneration in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Pubmed:26963343
- Stenotic Bicuspid and Tricuspid Aortic Valves - Micro-Computed Tomography and Biological Indices of Calcification.pubmed:28344201
- Effect of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy on Myocardial Fibrosis and Relevant Cytokines in a Canine Model With Experimental Heart Failure.pubmed:28127817
- Osteopontin stimulates matrix metalloproteinase expression through the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in rat temporomandibular joint and condylar chondrocytes.pubmed:28337262
- Targeted Microbiome Intervention by Microencapsulated Delayed-Release Niacin Beneficially Affects Insulin Sensitivity in Humanspubmed:29212824
- Icaritin induces MC3T3-E1 subclone14 cell differentiation through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling activation.pubmed:28742995
- Urine-Based Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease Identified Through Coupling Computational and Experimental MethodsPubmed:30040720
- Osteopontin, cardiovascular risk factors and carotid intima-Media thickness in chronic kidney diseaseid:233806
- In Situ Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide/Polydopamine/Sr2+ Nanosheets on Titanium Surfaces for Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem CellsDoi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.081
- Detection of proteins associated with extracellular matrix regulation in the aqueous humour of patients with primary glaucoma.Pubmed: 30994369
- Identification of urinary candidate biomarkers of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in patients with carcinomaPubmed: 31629959
- Inflammatory response to magnesium-based biodegradable implant materialsPubmed: 31610341
- Calcium Kidney Stones are Associated with Increased Risk of Carotid Atherosclerosis: the Link between Urinary Stone Risks, Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, and …Pubmed: 32182704
- Febuxostat attenuates vascular calcification induced by vitamin D3 plus nicotine in ratsPubmed: 33010420
- Osteoconductive potential of PLGA/bioglass composite biomaterials
- Structural Constraint of Osteopontin Facilitates Efficient Binding to CD4434070790
- Structural Changes and Detection of Liver Fibrosis¨CRelated Protein Levels in Coculture of Alveolar Echinococcosis-Protoscoleces and Human Hepatic Stellate cells
- Structural changes and expression of hepatic fibrosis-related proteins in coculture of Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces and human hepatic stellate …34857049
- Plasma Concentrations of New Biochemical Markers of Atherosclerosis in Patients with Dyslipidemia—A Pilot StudyPubmed:35743980