Multiplex Assay Kit for Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) 
Apo-A1; ApoA-1 Milano; ProapoA-I; Proapolipoprotein A-I; Truncated apolipoprotein A-I
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- UOM
- FOB US$ 472.00 US$ 490.00 US$ 517.00 US$ 553.00 US$ 590.00 US$ 644.00 US$ 726.00 US$ 907.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LMA519Po
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsFLIA Kit for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayCardiovascular biologyHepatology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 98-105 | 101 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-95 | 91 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 96-104 | 101 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 98-105% | 86-93% | 81-97% | 93-104% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-101% | 96-104% | 81-99% | 86-103% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-103% | 94-102% | 88-96% | 89-97% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:APOA1) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
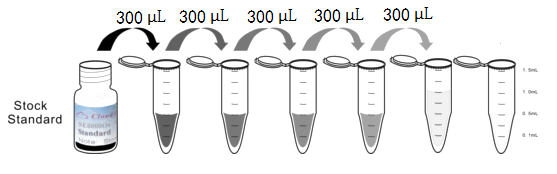
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
Test principle
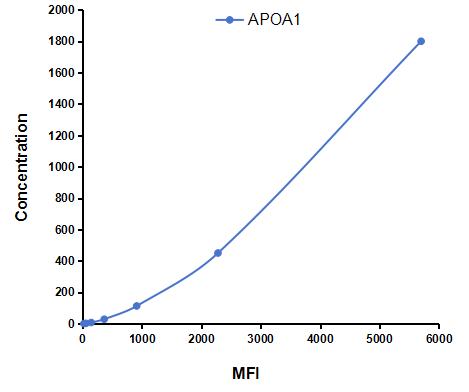
Analyte-specific antibodies are pre-coated onto color-coded microparticles. Microparticles, standards, and samples are pipetted into wells and the immobilized antibodies bind the analytes of interest. After washing away any unbound substances, a biotinylated antibody cocktail specific to the analytes of interest is added to each well. Following a wash to remove any unbound biotinylated antibody, Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin conjugate (Streptavidin-PE), which binds to the biotinylated detection antibodies, is added to each well. A final wash removes unbound Streptavidin-PE and the microparticles are resuspended in buffer and read using the Luminex or Bio-Plex analyzer.The MFI developed is proportional to the concentration of analytes of interest in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Endurance training enhances ABCA1 expression in rat small intestinePubMed: 19629515
- Effect of eight weeks of wrestling and circuit fitness training on Apo lipoportein A-I and lymphocyte ABCA1 gene expression in well-trained wrestler. Wrestling: source
- Treadmill exercise enhances ABCA1 expression in rat liverScienceDirect: S0006291X0701488X
- The Effect of Eight Weeks of Wrestling and Wrestling Technique Based Circuit Training on Lymphocyte ABCA1 Gene Expression and Plasma Apolipoprotein A-1Idosi: source
- Hepatic lipase- and endothelial lipase-deficiency in mice promotes macrophage-to-feces RCT and HDL antioxidant propertiesPubMed: 23328279
- The association of a distinct plasma proteomic profile with the cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion of Uyghur women: a 2D liquid-phase chromatography/mass spectrometry studyPubMed: 22458349
- MicroRNA-33 Deficiency Reduces the Progression of Atherosclerotic Plaque in ApoE?/? MicePubMed: PMC3540673
- Apolipoprotein AI Is a Potential Mediator of Remote Ischemic PreconditioningPlosone: Source
- DYRK1A overexpression decreases plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity and apolipoprotein AI levelsPubmed: 23920041
- Deficiency of Clusterin Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Pubmed: 24684302
- Corrective effects of hepatotoxicity by hepatic Dyrk1a gene delivery in mice with intermediate hyperhomocysteinemiaSciencedirect:S2214426915000026
- Anti-atherogenic properties of high-density lipoproteins in psychiatric patients before and after two months of atypical anti-psychotic therapyPubMed: 26253619
- Culturing of HepG2 cells with human serum improve their functionality and suitability in studies of lipid metabolismPubMed: 26515253
- Efficacy of tomato concentrates in mouse models of dyslipidemia and cancerPubMed: 26171234
- Differentially expressed urinary biomarkers in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndromePubMed: 26351173
- Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesisPubMed: 26279300
- Apolipoprotein AI inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesisPubmed:26279300
- Serum levels of 9α,11β-PGF2 and apolipoprotein A1 achieve high predictive power as biomarkers of anaphylaxis.pubmed:28378321
- Application of a new procedure for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry profiling of plasma amino acid-related metabolites and untargeted shotgun proteomics to identify mechanisms and biomarkers of calcific aortic stenosisS0021967317311858
- High-Density Lipoproteins Exert Pro-inflammatory Effects on Macrophages via Passive Cholesterol Depletion and PKC-NF-kB/STAT1-IRF1 Signalingpubmed:27866837
- Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb 761) on Serum Cholesterol Levels in Wild-type C57Bl/6 Mice10.15616/BSL.2017.23.2.80
- Enhanced Antiatherosclerotic Efficacy of Statin-Loaded Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein via Ganglioside GM1 Modificationabs:10.1021
- Wild Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenol extract reduces cholesterol accumulation and enhances antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivoPubmed:29580541
- Consumption of orange fermented beverage improves antioxidant status and reduces peroxidation lipid and inflammatory markers in healthy humansPubmed:29124773
- A membrane disrupting toxin from wasp venom underlies the molecular mechanism of tissue damagePubmed:29654869
- The effect of exenatide (a GLP-1 analog) and sitagliptin (a DPP-4 inhibitor) on plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) activity and concentration in?…Pubmed: 30768981
- High-intensity interval training has a greater effect on reverse cholesterol transport elements compared with moderate-intensity continuous training in obese male ratsPubmed: 31718266
- Systemic Alterations of Immune Response-Related Proteins during Glaucoma Development in the Murine Model DBA/2JPubmed: 32585848
- Pathology and Proteomics-Based Diagnosis of Localized Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Dogs and CatsPubmed: 32880234
- GP73 is a TBC-domain Rab GTPase-activating protein contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without obesity34853313
- Interplay of Obesity, Ethanol, and Contaminant Mixture on Clinical Profiles of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: Evidence from an Animal StudyPubmed:35429258
- Neuropeptide Y promotes hepatic apolipoprotein A1 synthesis and secretion through neuropeptide Y Y5 receptorPubmed:35660638
- Castanea mollissima shell polyphenols regulate JAK2 and PPARγ expression to suppress inflammation and lipid accumulation by inhibiting M1 macrophages …