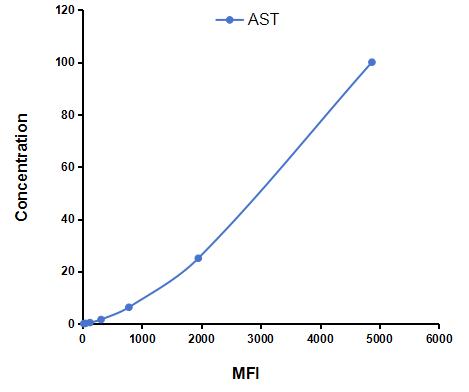
Multiplex Assay Kit for Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) 
cCAT; AAT; ASAT; SGOT; GOT1; Cysteine transaminase, cytoplasmic; Transaminase A; Aspartate Transaminase 1,Cytoplasmic; Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase 1,Soluble
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- UOM
- FOB US$ 427.00 US$ 443.00 US$ 468.00 US$ 501.00 US$ 534.00 US$ 583.00 US$ 657.00 US$ 821.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LMB214Mu
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsFLIA Kit for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseTumor immunityInfection immunityHepatology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 97-104 | 101 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 79-105 | 89 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 85-94 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 81-101% | 81-98% | 87-96% | 78-92% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-101% | 81-90% | 98-105% | 90-101% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-101% | 86-101% | 79-98% | 95-104% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:AST) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
Test principle
Analyte-specific antibodies are pre-coated onto color-coded microparticles. Microparticles, standards, and samples are pipetted into wells and the immobilized antibodies bind the analytes of interest. After washing away any unbound substances, a biotinylated antibody cocktail specific to the analytes of interest is added to each well. Following a wash to remove any unbound biotinylated antibody, Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin conjugate (Streptavidin-PE), which binds to the biotinylated detection antibodies, is added to each well. A final wash removes unbound Streptavidin-PE and the microparticles are resuspended in buffer and read using the Luminex or Bio-Plex analyzer.The MFI developed is proportional to the concentration of analytes of interest in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone ameliorates acute kidney injury by steroidogenic-dependent and -independent mechanismsPubMed: PMC3612362
- Pathogenesis of emerging severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in C57/BL6 mouse modelPubMed: PMC3382536
- Protective effect of Panax ginseng against N-acetyl-p-aminophenol-induced hepatotoxicity in ratsAcademicjournals: Source
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone ameliorates acute kidney injury by steroidogenic-dependent and-independent mechanismsPubmed: 23325074
- Protective effect of Et-1 receptor antagonist bosentan on paracetamol induced acute liver toxicity in ratsScienceDirect: S0014299914000235
- The P2X1 Receptor Is Required for Neutrophil Extravasation during Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lethal Endotoxemia in MicePubmed:25480563
- Assessing the Effect of Leptin on Liver Damage in Case of Hepatic Injury Associated with Paracetamol PoisoningPubMed: 26697061
- Advanced Studies in Clinical and Experimental Research in GastroenterologyPubmed:26955389
- Adiponectin protects the rats liver against chronic intermittent hypoxia induced injury throughAMP-activated protein kinase pathway.pubmed:27678302
- Modulation of gut microbiota contributes to curcumin-mediated attenuation of hepatic steatosis in ratspubmed:28341485
- Deletion of MCP-1 Impedes Pathogenesis of Acid Ceramidase DeficiencyPubmed:29379059
- A critical role of hepatitis B virus polymerase in cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and steatosisPubmed:29321963
- Hepatoprotective activity of Erythrina× neillii leaf extract and characterization of its phytoconstituentsPubmed: 28095910
- Hepatic pathology and altered gene transcription in a murine model of acid ceramidase deficiencyPubmed: 31186526
- Corticosterone-mediated microglia activation affects dendritic spine plasticity and motor learning functions in minimal hepatic encephalopathyPubmed: 31437533
- Liraglutide Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Rats Administered a High-Fat DietPubmed: 32149099
- Biological Safety and Biodistribution of Chitosan NanoparticlesPubmed: 32340313
- Effects of Tempol in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury
- Antimalarial Effect of the Total Glycosides of the Medicinal Plant, Ranunculus japonicus33925018
- Taraxasterol mitigates Con A-induced hepatitis in mice by suppressing interleukin-2 expression and its signaling in T lymphocytes34848154
- NFAT inhibitor 11R-VIVIT ameliorates mouse renal fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury34937917
- Water Specific MRI T1 Mapping for Evaluating Liver Inflammation Activity Grades in Rats With Methionine‐Choline‐Deficient Diet‐Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver …Pubmed:35212074
- Blockade of mIL‐6R alleviated lipopolysaccharide‐induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome by suppressing NF‐κB‐mediated Ccl2 expression and …Pubmed:35548710
- Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates autoimmune hepatitis in mice by blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activationPubmed:35605433