Multiplex Assay Kit for Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) 
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- UOM
- FOB US$ 405.00 US$ 420.00 US$ 443.00 US$ 475.00 US$ 506.00 US$ 552.00 US$ 622.00 US$ 778.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LMA176Mu
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsFLIA Kit for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayCardiovascular biology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 78-98 | 89 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 93-101 | 97 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-104 | 86 |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 80-104 | 90 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Collagen Type III (COL3) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 97-105% | 78-102% | 93-103% | 83-104% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-102% | 97-105% | 81-89% | 88-96% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 93-101% | 90-101% | 97-105% | 78-99% |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 97-105% | 88-96% | 87-95% | 91-102% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:COL3) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
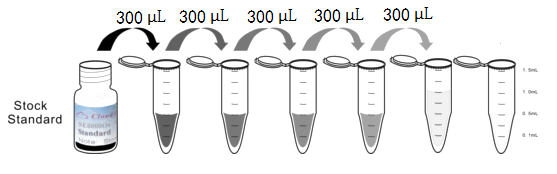
Test principle
Analyte-specific antibodies are pre-coated onto color-coded microparticles. Microparticles, standards, and samples are pipetted into wells and the immobilized antibodies bind the analytes of interest. After washing away any unbound substances, a biotinylated antibody cocktail specific to the analytes of interest is added to each well. Following a wash to remove any unbound biotinylated antibody, Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin conjugate (Streptavidin-PE), which binds to the biotinylated detection antibodies, is added to each well. A final wash removes unbound Streptavidin-PE and the microparticles are resuspended in buffer and read using the Luminex or Bio-Plex analyzer.The MFI developed is proportional to the concentration of analytes of interest in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Triptolide inhibits extracellular matrix protein synthesis by suppressing the Smad2 but not the MAPK pathway in TGF-β1-stimulated NRK-49F cellsOxfordJournals: 3180
- Serial cytokine levels during wound healing in rabbit maxillary sinus mucosaPubMed: 19958244
- Modification of collagen formation by mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human adipose tissue in culture and after autotransplantation for abdominal hernia plastyPubmed: 24319714
- In vitro tenocyte metabolism in aging and oestrogen deficiencySpringer: Source
- Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jellyPubmed: 24739658
- Effect of nandrolone and/or whey protein on the soleus muscle and testis of adult male albino ratsCom:Source
- Mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation, gene expression and protein production in human platelet-rich plasma-supplemented mediaPubmed:Pmc4130592
- Metabolic and cytoprotective effects of in vivo peri-patellar hyaluronic acid injections in cultured tenocytesPubmed:25333747
- Establishing principles of macromolecular crowding for in vitro fibrosis research of the vocal fold lamina propriaPubmed:25545625
- KLF15 is an essential negative regulatory factor for the cardiac remodeling response to pressure overloadPubmed:25633973
- The skin remodeling in type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance animal modelsPubMed: 26047379
- The skin remodeling in type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance animal models.PubMed: 26047379
- Comparative Analysis of the Extracellular Matrix Composition in Proliferating and Involuted Infantile HemangiomasPubMed: 26430624
- Pituitary tumor transforming gene as a novel regulatory factor of liver fibrosisPubMed: 25936962
- SVVYGLR motif of the thrombin-cleaved N-terminal osteopontin fragment enhances the synthesis of collagen type III in myocardial fibrosisPubMed: 26112906
- KLF16 Is an Essential Negative Regulatory Factor for the Cardiac Remodeling Response to Pressure OverloadPubMed: 25633973
- Uighur medicine abnormal savda munzip (ASMq) suppresses expression of collagen and TGF-β1 with concomitant induce Smad7 in human hypertrophic scar …PubMed: 26309506
- IL-17A mediates inflammatory and tissue remodelling events in early human tendinopathyPubmed:27263531
- Інфаркт міокарда, ускладнений аневризмою лівого шлуночка: клінічні і структурно-функціональні особливості перебігу, діагностичні, терапевтичні та прогностичні аспектиbitstream:123456789
- Plasma LncRNA-ATB, a Potential Biomarker for Diagnosis of Patients with Coal Workers'Pneumoconiosis: A Case-Control Study.pubmed:27556453
- Saikosaponin d induces cell death through caspase-3-dependent, caspase-3-independent andmitochondrial pathways in mammalian hepatic stellate cells.pubmed:27461108
- Genomic reprograming analysis of the Mesothelial to Mesenchymal Transition identifies biomarkers in peritoneal dialysis patients.pubmed:28327551
- Saikosaponin a Induces Apoptosis through Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway in Hepatic Stellate Cellspubmed:28231747
- Crystalline Silica Promotes Rat Fibrocyte Differentiation in Vitro, and Fibrocytes Participate in Silicosis in Vivopubmed:29081339
- Effects of the (Pro) renin Receptor on Cardiac Remodeling and Function in a Rat Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy Model via the PRR-ERK1/2-NOX4 Pathway
- Effect of proinflammatory cytokines on endometrial collagen and metallopeptidase expression during the course of equine endometrosisPubmed: 31265984
- Pantoea agglomerans chronic exposure induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lung epithelial cells and mice lungsPubmed: 32146192
- Distinct differences in hypoxic responses between human oral mucosa and skin fibroblasts in a 3D collagen matrixPubmed: 32588253
- Tissue-Engineered Decellularized Allografts for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
- Enhanced cell survival and therapeutic benefits of IL-10-expressing multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells for muscular dystrophy33541428
- Cell sheet technology: Influence of culture conditions on in vitro©\cultivated corneal stromal tissue for regenerative therapies of the ocular surface33538123
- Beneficial impact of cathelicidin on hypersensitivity pneumonitis treatment¡ªIn vivo studies33999928
- Uncarboxylated osteocalcin alleviates the inhibitory effect of high glucose on osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow¨Cderived mesenchymal stem?¡33906607
- Early diagnosis of myocardial fibrosis in patients with epicardial obesity
- Manuscript title Microparticles Containing MiR-625-5p In Coronary Artery Reduce Myocardial Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction