Multiplex Assay Kit for Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) 
CD138; SDC; SYND1; Syndecan Proteoglycan 1
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- UOM
- FOB US$ 498.00 US$ 517.00 US$ 546.00 US$ 584.00 US$ 623.00 US$ 680.00 US$ 766.00 US$ 958.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LMB966Po
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsFLIA Kit for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunityInfection immunityImmunodeficiency
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 83-93 | 87 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 79-89 | 82 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 84-101 | 96 |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 86-101 | 90 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
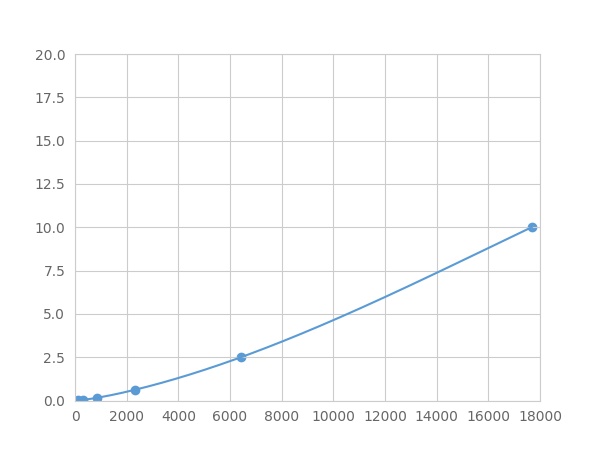
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Syndecan 1 (SDC1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 78-105% | 95-102% | 95-103% | 90-104% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 85-94% | 78-94% | 89-97% | 94-101% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-98% | 78-94% | 82-95% | 94-101% |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 96-103% | 94-102% | 94-101% | 78-91% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:SDC1) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
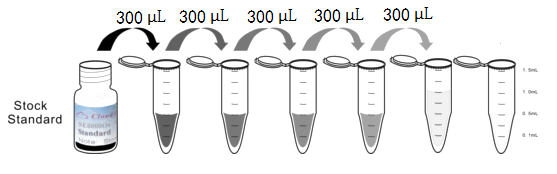
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
Test principle
Analyte-specific antibodies are pre-coated onto color-coded microparticles. Microparticles, standards, and samples are pipetted into wells and the immobilized antibodies bind the analytes of interest. After washing away any unbound substances, a biotinylated antibody cocktail specific to the analytes of interest is added to each well. Following a wash to remove any unbound biotinylated antibody, Streptavidin-Phycoerythrin conjugate (Streptavidin-PE), which binds to the biotinylated detection antibodies, is added to each well. A final wash removes unbound Streptavidin-PE and the microparticles are resuspended in buffer and read using the Luminex or Bio-Plex analyzer.The MFI developed is proportional to the concentration of analytes of interest in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Increased level of soluble syndecan-1 in serum correlates with myocardial expression in a rat model of myocardial infarctionSpringerLink: a201w3l18k257462
- Sdc1 Overexpression Inhibits the p38 MAPK Pathway and Lessens Fibrotic Ventricular Remodeling in MI RatsSpringer: Source
- Damage of the endothelial glycocalyx in chronic kidney diseasePubmed:24727235
- Effect of valproic acid and injury on lesion size and endothelial glycocalyx shedding in a rodent model of isolated traumatic brain injuryPubmed:25058256
- Impairment of the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Cardiogenic Shock and its Prognostic RelevancePubmed:25692257
- Dexamethasone Suppressed LPS-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase and Its Effect on Endothelial Glycocalyx SheddingPubMed: 26199464
- Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-B Protects Rat Cardiac Allografts From Ischemia-reperfusion Injury.PubMed: 26371596
- Dual antiplatelet and anticoagulant APAC prevents experimental ischemia–reperfusion-induced acute kidney injurypubmed:27405618
- Endothelial glycocalyx layer shedding following lung resectionpubmed:27643669
- Resuscitation with Pooled and Pathogen-Reduced Plasma Attenuates the Increase in Brain Water Content following Traumatic Brain Injury and Hemorrhagic Shock in Rats10.1089
- Resuscitation with pooled and pathogen-reduced plasma attenuates the increase in brain water content following traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic shock in rats the rat.doi/10.1089/neu.2016.4574
- Volume kinetics of Ringer's lactate solution in acute inflammatory disease10.1016:j.bja.2018.04.023
- MPO (myeloperoxidase) reduces endothelial glycocalyx thickness dependent on its cationic chargePubmed:29903730
- Plasma resuscitation improved survival in a cecal ligation and puncture rat model of sepsisPubmed:28591008
- Experimental models of endotheliopathy: impact of shock severityPubmed:28697004
- Effects of propranolol and clonidine on brain edema, blood-brain barrier permeability, and endothelial glycocalyx disruption after fluid percussion brain injury in the ratPubmed:28930945
- The Endothelial Glycocalyx in the Peritoneal Microcirculation of Rats with Chronic Kidney Failure Exposed to Dialysis Solutions173015_06.pdf
- Plasma ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in burn injuryDoi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.08.027
- Dexmedetomidine preserves the endothelial glycocalyx and improves survival in a rat heatstroke modelPubmed: 30374889
- Postoperative microcirculatory perfusion and endothelial glycocalyx shedding following cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypassPubmed: 30687934
- Microvascular alterations during cardiac surgery using a heparin or phosphorylcholine coated circuitPubmed: 31787433
- Increased syndecan-1 and glypican-3 predict poor perinatal outcome and treatment resistance in intrahepatic cholestasis: Syndecan-1, glypican-3 and ICPPubmed: 31919038
- Heparin Binding Protein and Endothelial Glycocalyx Markers in Severe COVID-19–A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
- Newly Developed Recombinant Antithrombin Protects the Endothelial Glycocalyx in an Endotoxin-Induced Rat Model of Sepsis33375342
- Effect of liraglutide on microcirculation in rat model with absolute insulin deficiency34119534
- The effect of pre-operative methylprednisolone on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo …34423832
- Inhalation of 2% hydrogen improves survival rate and attenuates shedding of vascular endothelial glycocalyx in rats with heat stroke34524269
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses serum syndecan-1 elevation and improves survival in a rat hemorrhagic shock modelPubmed:35110424
- Resuscitation of hemorrhagic shock using normal saline does not damage the glycocalyx in the immediate resuscitation phase