Mini Samples ELISA Kit for Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) 
LOS; Lipoglycans; Lipooligosaccharide; Lipo-Oligosaccharide; Endotoxin
- UOM
- FOB US$ 559.00 US$ 798.00 US$ 3,591.00 US$ 6,783.00 US$ 55,860.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.MEB526Ge
- Organism SpeciesPan-species (General) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- Category
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 81-93 | 86 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 88-102 | 95 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 81-94 | 90 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 88-95% | 89-96% | 87-102% | 79-98% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 91-99% | 91-105% | 82-93% | 96-104% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-99% | 80-101% | 90-97% | 90-104% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×6mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×6mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×3mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×10mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
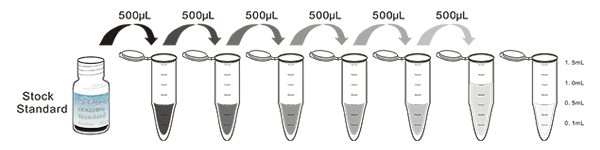
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 25µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 25μL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 50µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 25µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
Test principle
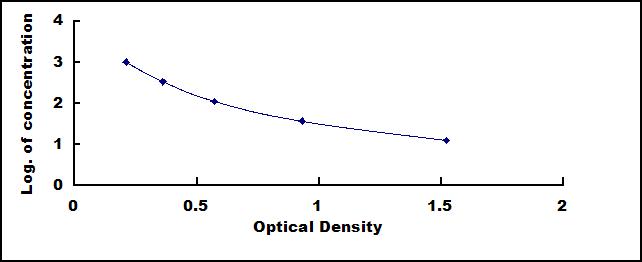
This assay employs the competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay technique. A monoclonal antibody specific to Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) has been pre-coated onto a microplate. A competitive inhibition reaction is launched between biotin labeled Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and unlabeled Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (Standards or samples) with the pre-coated antibody specific to Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). After incubation the unbound conjugate is washed off. Next, avidin conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to each microplate well and incubated. The amount of bound HRP conjugate is reverse proportional to the concentration of Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the sample. After addition of the substrate solution, the intensity of color developed is reverse proportional to the concentration of Mini Samples Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the sample.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Particulate matter air pollution disrupts endothelial cell barrier via calpain-mediated tight junction protein degradationPubMed: 22931549
- Hemoglobin induces inflammation after preterm intraventricular hemorrhage by methemoglobin formationPubMed: PMC3750409
- Antidiabetic effect of Lactobacillus casei CCFM0412 in high-fat-fed, streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice ScienceDirect: S0899900714001567
- Effects of Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 on Hepatic Steatosis in Zucker RatsPubmed:24852284
- Immunological Activity Difference between Native Calreticulin Monomers and OligomersPubmed:25171171
- Antidiabetic effect of Lactobacillus casei CCFM0412 on mice with type 2 diabetes induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocinPubmed:25102821
- Oral administration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM0528 improves glucose tolerance and cytokine secretion in high-fat-fed, streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic …Sciencedirect:S1756464614002138
- Is there interaction between gut microbial profile and cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease patients?PubMed: 25865191
- Effects of probiotics (cultured Lactobacillus subtilis/Streptococcus faecium) in the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis: randomized-controlled multicenter studyPubMed: 26302024
- The effects of female sexual steroids on gastric function and barrier resistance of gastrointestinal tract following traumatic brain injuryPubMed: 25709342
- Fecal menaquinone profiles of overweight adults are associated with gut microbiota composition during a gut microbiota–targeted dietary interventionPubMed26016865 :
- Deficiency of intestinal mucin-2 protects mice from diet-induced fatty liver disease and obesityPubMed: 26702135
- Oxymatrine attenuates CCl 4-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TLR4-dependent inflammatory and TGF-β1 signaling pathwaysPubmed:27179304
- Portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis is not associated with intestinal barrier disruption or increased platelet aggregabilityPubmed:27160816
- Administration of probiotic mixture DM# 1 ameliorated 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis and dysbiosis in ratsscience:S0899900716300740
- Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 alleviates liver cirrhosis via improvement of the dysfunctional Cavia (Guinea pig )t-liver axis in ratsPubmed:27056726
- Food combination based on a pre-hispanic Mexican diet decreases metabolic and cognitive abnormalities and gut microbiota dysbiosis caused by a sucrose-enriched high-fat diet in rats.pubmed:27352915
- Administration of probiotic mixture DM# 1 ameliorated 5-fluorouracil–induced intestinal mucositis and dysbiosis in ratsarticle:S0899-9007(16)30074-0
- Modulation of gut microbiota contributes to curcumin-mediated attenuation of hepatic steatosis in ratspubmed:28341485
- Relationship between plasma levels of zonulin, bacterial lipopolysaccharides, d‑lactate and markers of inflammation in haemodialysis patientspubmed:28044237
- Administration of probiotic mixture DM#1 ameliorated 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis and dysbiosis in ratspubmed:27427511
- Co-supplementation of isomalto-oligosaccharides potentiates metabolic health benefits of polyphenol-rich cranberry extract in high fat diet-fed mice via enhanced gut butyrate productiondoi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1561-5
- Coadministration of isomalto-oligosaccharides augments metabolic health benefits of cinnamaldehyde in high fat diet fed mice.pubmed:28799667
- Nopal (Opuntia ficus indica) protects from metabolic endotoxemia by modifying gut microbiota in obese rats fed high fat/sucrose diet.pubmed:28680065
- Gastric acid suppression promotes alcoholic liver disease by inducing overgrowth of intestinal Enterococcus.pubmed:29038503
- Food combination based on a pre-hispanic Mexican diet decreases metabolic and cognitive abnormalities and gut microbiota dysbiosis caused by a sucrose-enriched high-fat diet in rats10.1002/mnfr.201501023
- Differential Effect of Sucrose and Fructose in Combination with a High Fat Diet on Intestinal Microbiota and Kidney Oxidative Stresspubmed:28420148
- House Dust Mites Induce Production of Endothelin-1 and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Keratinocytes via Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 Activationpubmed:28586781
- Long‐Term Genistein Consumption Modifies Gut Microbiota, Improving Glucose Metabolism, Metabolic Endotoxaemia and Cognitive Function in Mice Fed a High‐Fat …Pubmed:29979819
- IgG Immunocomplexes Sensitize Human Monocytes for Inflammatory Hyperactivity via Transcriptomic and Epigenetic Reprogramming in Rheumatoid ArthritisPubmed:29712771
- AWRK6, A Synthetic Cationic Peptide Derived from Antimicrobial Peptide Dybowskin-2CDYa, Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory ResponsePubmed:29463000
- Effects of probiotic supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers and uremic toxins in non-dialysis chronic kidney patients: A double-blind, randomized, placebo …10.1016:j.jff.2018.05.018
- Effect of systemic administration of lipopolysaccharides derived from on gene expression in mice kidneyPubmed:29388058
- The Role of Intestinal C‐type Regenerating Islet Derived‐3 Lectins for Nonalcoholic SteatohepatitisPubmed:29619418
- アトピー性皮膚炎の痒みの発症機序に関する研究
- Repression of TXNIP–NLRP3 axis restores intestinal barrier function via inhibition of myeloperoxidase activity and oxidative stress in nonalcoholic steatohepatitisPubmed: 30387131
- Bioactive Food Abates Metabolic and Synaptic Alterations by Modulation of Gut Microbiota in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's DiseasePubmed: 30475761
- Evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 on biomarkers of inflammation, cardiovascular risk and liver steatosis in obese adults with metabolic …Pubmed: 30453950
- Effects of fecal microbiota transplantation and joint application of probiotics on rats with alcoholic liver disease
- Lactobacillus plantarum helps to suppress body weight gain, improve serum lipid profile and ameliorate low-grade inflammation in mice administered with glycerol …Doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.12.015
- A combination of Pueraria lobata and Silybum marianum (L.) Gaerth protects against alcoholic liver disease in mice
- Megasphaera elsdenii Lactate Degradation Pattern Shifts in Rumen Acidosis Models
- Intestinal iNKT Cells Migrate to Liver and Contribute to Hepatocyte Apoptosis During Alcoholic Liver DiseasePubmed: 30817180
- Influence of poly (I: C) variability on thermoregulation, immune responses and pregnancy outcomes in mouse models of maternal immune activation
- Hepatic progenitor cell activation is induced by the depletion of the gut microbiome in micePubmed: 31094067
- Additional Effect of Dietary Fiber in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Metformin and Sulfonylurea: An Open-Label, Pilot Trial
- Lipopolysaccharide in systemic circulation induces activation of inflammatory response and oxidative stress in cardiorenal syndrome type 1Pubmed: 31006081
- Intestinal injury and gut permeability in sickle cell diseasePubmed: 31146745
- Glycerol Monolaurate‐Mediated Attenuation of Metabolic Syndrome is Associated with the Modulation of Gut Microbiota in High Fat diet‐fed MicePubmed: 31318165
- Probiotics modulate the microbiota–gut–brain axis and improve memory deficits in aged SAMP8 mice
- High-dose Glycerol Monolaurate Up-Regulated Beneficial Indigenous Microbiota without Inducing Metabolic Dysfunction and Systemic Inflammation: New Insights …
- Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 Reduces Inflammatory Biomarkers and Modifies the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: The PROSIR StudyPubmed: 31370223
- The Combination of Ilexhainanoside D and Ilexsaponin A1 Reduces Liver Inflammation and Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in Mice with High-fat Diet-induced …
- Effects of sinomenine in LPS‐associated diseases are related to inhibition of LBP, Mac‐1, and L‐selectin levelsPubmed: 31490576
- Improvement of Lipoprotein Profile and Metabolic Endotoxemia by a Lifestyle Intervention That Modifies the Gut Microbiota in Subjects With Metabolic SyndromePubmed: 31451009
- Depolymerized RG-I enriched pectin from citrus segment membrane modulates gut microbiota, increases SCFAs production, promotes the growth of Bifidobacterium …Pubmed: 31778135
- Gut Dysbiosis with Minimal enteritis induced by High temperature and HumidityPubmed: 31822775
- Ochratoxin A induces liver inflammation: involvement of intestinal microbiotaPubmed: 31779704
- Compromised Ileal Mucus Barrier Due to Impaired Epithelial Homeostasis Caused by Notch1 Signaling in Cirrhotic RatsPubmed: 32144600
- Liraglutide Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Rats Administered a High-Fat DietPubmed: 32149099
- Effect of resveratrol on intestinal tight junction proteins and the gut microbiome in high-fat diet-fed insulin resistant micePubmed: 32306796
- The Gut Microbial Diversity of Newly Diagnosed Diabetics but Not of Prediabetics Is Significantly Different from That of Healthy NondiabeticsPubmed: 32234773
- Disease-Specific Autoantibodies Induce Trained Immunity in RA Synovial Tissues and Its Gene Signature Correlates with the Response to Clinical TherapyPubmed: 33082707
- The development of metabolic endotoxemia is dependent on the type of sweetener and the presence of saturated fat in the dietPubmed: 32804018
- Aplysin Retards Pancreatic Necrosis and Inflammatory Responses in NOD Mice by Stabilizing Intestinal Barriers and Regulating Gut Microbial CompositionPubmed: 32801992
- Gut-liver axis modulation in fructose-fed mice: a role for PPAR-alpha and linagliptinPubmed: 32698143
- The colonic mucosa-associated microbiome in SIV infection: shift towards Bacteroidetes coincides with mucosal CD4+ T cell depletion and enterocyte damagePubmed: 32616803
- Consumption of Cooked Black Beans Stimulates a Cluster of Some Clostridia Class Bacteria Decreasing Inflammatory Response and Improving Insulin SensitivityPubmed: 32340138
- Pasteurella multocida Pm0442 Affects Virulence Gene Expression and Targets TLR2 to Induce Inflammatory ResponsesPubmed: 32922380
- RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF PERITONITIS IN PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PATIENTS
- Age-related cognitive decline is associated with microbiota-gut-brain axis disorders and neuroinflammation in mice33422597
- IgG immunocomplexes drive the differentiation of a novel subset of osteoclasts independent of RANKL and inflammatory cytokines33651383
- Bioengineered bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles as a versatile antigen display platform for tumor vaccination via Plug-and-Display technology33824314
- The Relationship between Low Serum Vitamin D Levels and Altered Intestinal Barrier Function in Patients with IBS Diarrhoea Undergoing a Long-Term Low-FODMAP33801020
- Consumption of soybean or olive oil at recommended concentrations increased the intestinal microbiota diversity and insulin sensitivity and prevented fatty liver?¡33915261
- Somatization in patients with predominant diarrhoea irritable bowel syndrome: the role of the intestinal barrier function and integrity34022802
- Inhibition of cyclooxygenase©\2 enhanced intestinal epithelial homeostasis via suppressing ¦Â©\catenin signalling pathway in experimental liver fibrosis34145945
- Tissue transglutaminase is involved in the inflammatory processes of active chronic gastritis17539352
- ¡°Adjusting Internal Organs and Dredging Channel¡± Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Regulating the Intestinal?¡34135611
- Melatonin ameliorates ochratoxin A induced liver inflammation, oxidative stress and mitophagy in mice involving in intestinal microbiota and restoring the?¡33359973
- A Perfusion Bioreactor for Longitudinal Monitoring of Bioengineered Liver Constructs33494337
- A rise in Proteobacteria is an indicator of gut-liver axis-mediated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fructose-fed adult mice34130208
- Indole-3-propionic Acid-aggravated CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis via the TGF-¦Â1/Smads Signaling Pathway
- Gut barrier and microbiota changes with glycine and branched‐chain amino acid supplementation in chronic haemodialysis patients34535959
- Intestinal pathophysiological abnormalities in steady state and after vaso‐occlusive crisis in murine sickle cell disease34632582
- Inflammatory alveolar macrophage-derived microvesicles damage lung epithelial cells and induce lung injury34740720
- Allicin Ameliorates Intestinal Barrier Damage via Microbiota-Regulated Short-Chain Fatty Acids-TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Cascade Response in Acrylamide-Induced Rats34694121
- Ligature induced periodontitis in rats causes gut dysbiosis leading to hepatic injury through SCD1/AMPK signalling pathway34813797
- Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability34896249
- Psychological and Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Undergoing a Low-FODMAP Diet: The Role of the Intestinal Barrier34371976
- Lactobacillus casei relieves liver injury by regulating immunity and suppression of the enterogenic endotoxin‐induced inflammatory response in rats cotreated with …34646510
- ALLICIN, A DIETARY TRPA1 AGONIST, PREVENTS HIGH FAT DIET-INDUCED DYSREGULATION OF GUT HORMONES AND ASSOCIATED COMPLICATIONS34705006
- Indole-3-propionic Acid-aggravated CCl34966655
- The Outer Membrane Vesicles of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Activate Chicken Immune Cells through Lipopolysaccharides and Membrane ProteinsPubmed:35335663
- Biomimic Trained Immunity‐MSCs Delivery Microcarriers for Acute Liver Failure RegenerationPubmed:35411651
- Effects of the maternal gut microbiome and gut-placental axis on melatonin efficacy in alleviating cadmium-induced fetal growth restrictionPubmed:35487173
- Gut dysbiosis promotes prostate cancer progression and docetaxel resistance via activating NF-κB-IL6-STAT3 axisPubmed:35710492
- The Role of Aeromonas-Goblet Cell Interactions in Melatonin-Mediated Improvements in Sleep Deprivation-Induced ColitisPubmed:35355860
- Co-interventions with Clostridium butyrate and soluble dietary fiber targeting gut microbiota improve MAFLD via the Acly/Nrf2/NFκ B signaling pathwayPubmed:35543143
- Vascular Calcification and the Gut and Blood Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis: A Pilot Study