Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI)
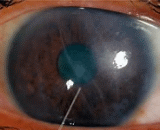
Although leukocyte-mediated cell injury has long been suggested as a major mechanism of general tissue injury in acute and chronic inflammation, only limited data have been developed to directly implicate leukocytes in ocular tissue injury. In an effort to unravel the role and mechanisms of leukocyte-mediated injury to the cornea, an isolated corneal cup model was developed. For this model, peripheral bovine leukocytes were added to isolated bovine corneal cultures (corneal cup) in vitro, after which endothelial cell damage and death were evaluated morphologically. In general, corneal endothelial cell swelling was observed within 5-10 minutes after leukocyte exposure, followed by detachment of the corneal endothelium at a 30-75-minute interval.
Organism species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Disease model DSI646Mu01 Mouse Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Disease model DSI646Mu02 Mouse Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Disease model DSI646Ra01 Rat Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Disease model DSI646Ra02 Rat Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Cavia (Guinea pig )
- Disease model DSI646Gu01 Cavia Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Disease model DSI646Gu02 Cavia Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Disease model DSI646Rb01 Rabbit Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Disease model DSI646Rb02 Rabbit Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Canis familiaris; Canine (Dog)
- Disease model DSI646Ca01 Canine Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Disease model DSI646Ca02 Canine Model for Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Corneal Endothelial Injury (CEI) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer


