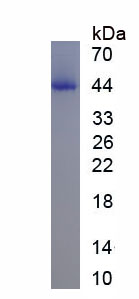
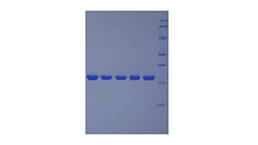
Active Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) 
ACEH; ACEII; ACE-II; Peptidyl-Dipeptidase A; ACE-related carboxypeptidase; Angiotensin-converting enzyme homolog; Metalloprotease MPROT15
- UOM
- FOB US$ 215.00 US$ 538.00 US$ 1,076.00 US$ 3,228.00 US$ 8,070.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APB886Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseMetabolic pathwayEndocrinologyCardiovascular biologyNeuro scienceHepatology
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point7.2
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
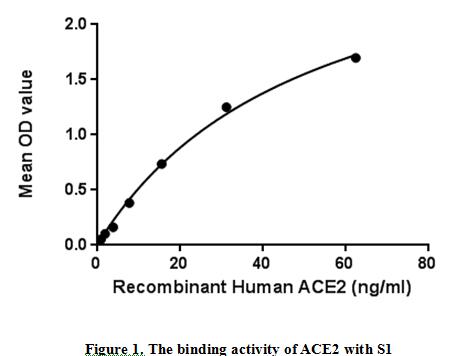
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), as a transmembrane protein, serves as the main entry point into cells for some coronaviruses, including HCoV-NL63, SARS-CoV , and SARS-CoV-2 . More specifically, the binding of the spike S1 protein of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 to the enzymatic domain of ACE2 on the surface of cells results in endocytosis and translocation of both the virusand the enzyme into endosomes located within cells. Besides, recent studies show that spike (S) proteins of 2019-nCoV and SARS-CoV may use the same host cell receptor called angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) for entering into host cells, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human ACE2 and recombinant Spike glycoprotein(S1). Briefly, ACE2 were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100μl were then transferred to S1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-ACE2 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of ACE2 and S1 was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Overexpression Remarkably Ameliorated Glomerular Injury in a Rat Model of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Comparison with ACE InhibitionMolMed: 10_11_liu
- Plasma Levels of Angiotensin-Converting Enzymes 1 and 2 and AGTR2 (T1247G and A5235G) Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated to Breast Cancer Progression.Scirp: Source
- ACE2 activation by xanthenone prevents leptin-induced increases in blood pressure and proteinuria during pregnancy in Sprague-Dawley ratsPubmed:25205467
- Angiotensin converting enzymes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndromeContent: 3
- Application of a new procedure for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry profiling of plasma amino acid-related metabolites and untargeted shotgun proteomics to identify mechanisms and biomarkers of calcific aortic stenosisS0021967317311858
- Relationship between genetic variants of ACE2 gene and circulating levels of ACE2 and its metabolites.pubmed:28895159
- Lipoxin A attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via activation of the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axisPubmed:29969931
- Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 levels on postoperative pneumonia after esophagectomyPubmed:29506841
- Could cardioprotective effect of ACE2 activator “diminazene aceturate” is more potent than ACE inhibitor “Enalapril” on acute myocardial infarction in rats?Pubmed: 30840489
- Angiotensin-converting enzymes in acute respiratory distress syndrome
- AVE 0991 Attenuates Pyroptosis and Liver Damage after Heatstroke by Inhibiting the ROS-NLRP3 Inflammatory Signalling Pathway
- Relationship between circulating levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin-(1–7)-MAS axis and coronary heart diseasePubmed: 31359146
- Alteration and association between serum ACE2/angiotensin (1-7)/Mas axis and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: A pilot studyPubmed: 32756181
- Equilibrium Angiotensin Metabolite Profiling in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Indicates Angiotensin Converting Enzyme InhibitionPubmed: 32628511
- Determinants of soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 concentrations in adult patients with complex congenital heart disease33280062
- Pattern of circulating SARS©\CoV©\2©\specific antibody©\secreting and memory B©\cell generation in patients with acute COVID©\1933552508
- Novel transgenic mice with Cre-dependent co-expression of GFP and human ACE2: a safe tool for study of COVID-19 pathogenesis33855640
- Different Neutralization Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Cell-to-Cell and Cell-Free Modes of Infection to Convalescent Sera
- Immunoreactivity of the SARS-CoV-2 entry proteins ACE-2 and TMPRSS-2 in murine models of hormonal manipulation, ageing, and cardiac injury34907257
- Angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 and Transmembrane protease serine 2 in female and male patients with end‐stage kidney diseasePubmed:35366343
- Ramipril Reduces Acylcarnitines and Distinctly Increases Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expression in Lungs of RatsPubmed:35448480