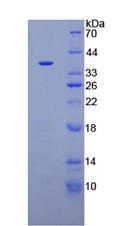
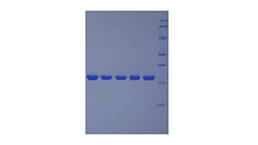
Active Annexin V (ANXA5) 
ANX5; ENX2; PP4; PAP-I; CBP-I; Anchorin CII; Calphobindin I; Endonexin II; Lipocortin V; Placental anticoagulant protein 4; Thromboplastin inhibitor; Vascular anticoagulant-alpha
- UOM
- FOB US$ 228.00 US$ 570.00 US$ 1,140.00 US$ 3,420.00 US$ 8,550.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA259Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryApoptosisHematology
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point5.1
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
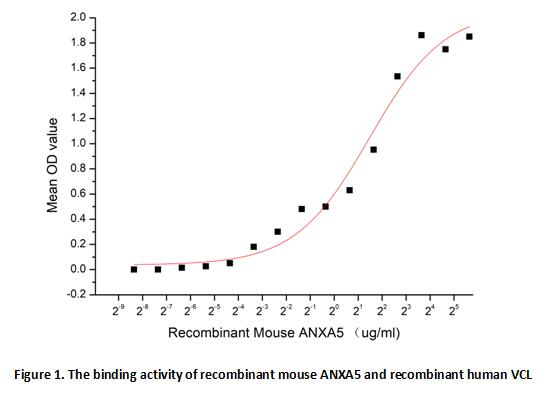
Annexin V (ANXA5) is a multifunctional protein that is highly expressed on the apical surfaces of syncytiotrophoblasts, and plays an important role in haemostatic regulations, maintaining blood fluidity of the placenta. Lower ANXA5 levels have been observed in M2/ANXA5 haplotype carrying chorion. The association found between the maternal carriage of the M2/ANXA5 haplotype and an elevated risk of IUGR and/or PE supports the hypothesis that carrier status of this haplotype and the consequently reduced placental ANXA5 expression might be responsible, at least partially, for the onset of these gestational vascular complications. ANXA5 could be used as a biomarker for the early detection of PE and for the prediction of its severity. ANXA5 as an embryonic anticoagulant that appears deficient in contiguous specter of thrombophilia-related pregnancy complications culminating more frequently in miscarriage in a maternal M2 carrier background. Besides, Vinculin (VCL) has been identified as an interactor of ANXA5, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant mouse ANXA5 and recombinant human VCL. Briefly, ANXA5 were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 μl were then transferred to VCL-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 1h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-ANXA5 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 5 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450 nm immediately. The binding activity of recombinant mouse ANXA5 and recombinant human VCL was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner, the EC50 was 2.79 ug/ml.
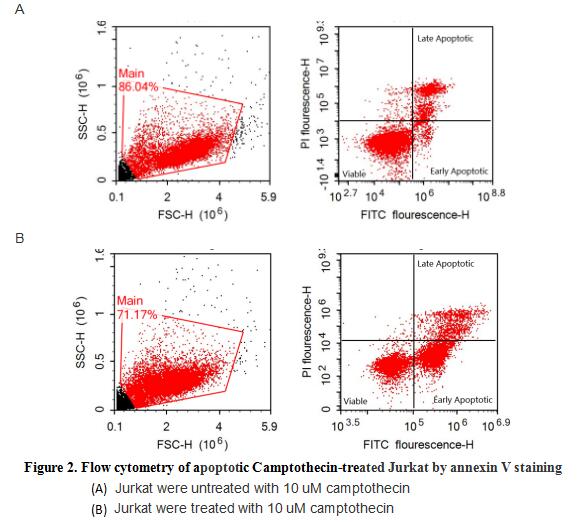
Annexin V (ANXA5) is a multifunctional protein that is highly expressed on the apical surfaces of syncytiotrophoblasts, and plays an important role in haemostatic regulations, maintaining blood fluidity of the placenta. Lower ANXA5 levels have been observed in M2/ANXA5 haplotype carrying chorion. The association found between the maternal carriage of the M2/ANXA5 haplotype and an elevated risk of IUGR and/or PE supports the hypothesis that carrier status of this haplotype and the consequently reduced placental ANXA5 expression might be responsible, at least partially, for the onset of these gestational vascular complications. Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid binding protein that can be used to bind Phosphatidylserine (PS) during an early apoptosis event where the PS becomes exposed at the cell surface. Jurkat cells were treated with 10 uM camptothecin for 4h, 2*105 cells which were resuspended in binding buffer were stained with 5 ug recombinant mouse Annexin V-FITC and 10 ul Propidium iodide (PI) for 20min in dark room temperature. The flow cytometry was used to detect the early apoptotic and late apoptotic of camptothecin-treated Jurkat cells (Figure 2), the combination of Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide allows for the distinction between early apoptotic cells (Annexin V-FITC positive and propidium iodide negative), late apoptotic and/or necrotic cells (Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide positive), and viable cells (unstained). Thus, the recombinant mouse Annexin V-FITC can bind Phosphatidylserine (PS) at early apoptosis of Jurkat.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Markers of apoptotic dysfunctions in schizophreniaPubmed: 24466757
- Involvement of Anomalous Apoptosis in Impairments to Synaptic Plasticity in Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderSpringer: Source
- Collectins, C3 complement protein, annexin V and C-reactive protein in acute ischemic stroke: interrelation and implication to upregulated apoptosis and inflammationSmartscitech: Source
- Annexin A5 Protein as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of AsthmaPubmed: 30182154