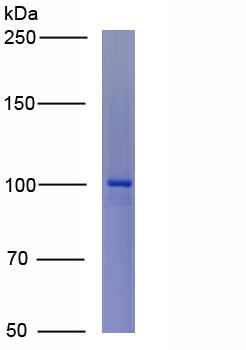
Active Amiloride Binding Protein 1 (ABP1) 
AOC1; DAO; KAO; Histaminase; Kidney amine oxidase; Diamine Oxidase; Amiloride-sensitive amine oxidase; Amine oxidase copper domain-containing protein 1
- UOM
- FOB US$ 301.00 US$ 752.00 US$ 1,504.00 US$ 4,512.00 US$ 11,280.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA656Hu61
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & Kinase
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point6.6
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
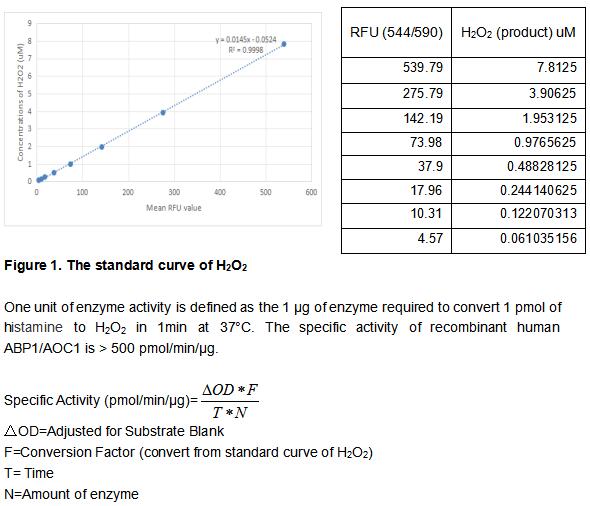
Amiloride binding protein (ABP1), also known as amine oxidase copper domain-containing protein 1 (AOC1), is an approximately 110 kDa member of the copper-containing amine oxidase family. ABP1 is a glycosylated enzyme that forms disulfide-linked homodimers. It is stored in cytoplasmic granules of epithelial cells in the kidney, placenta, uterus, lung, and intestine, and its extracellular release can be induced by heparin. ABP1 exhibits a substrate preference for histamine and putrescine, generating hydrogen peroxide and ammonia in an oxidative deamination reaction. ABP1 activity plays an important role in the catabolism of histamine and other bioactive polyamines. The activity of recombinant human ABP1 was measured by its ability to produce hydrogen peroxide during the oxidation of histamine. The reaction was performed in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5 (assay buffer), initiated by addition 50 μL of various concentrations of ABP1 (diluted by assay buffer) to 50 µl substrate mixture of 10 uM histamine, 2 units/mL HRP and 100 µM AUR. Read at excitation and emission wavelengths of 544 nm and 590 nm (top read), respectively in kinetic mode for 5 minutes.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.6) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
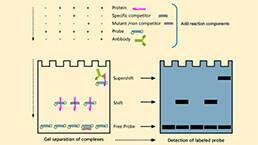 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
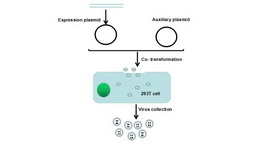 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
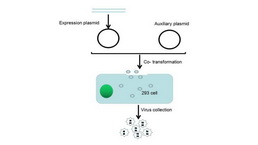 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Effects of copper-exchanged montmorillonite, as alternative to antibiotic, on diarrhea, intestinal permeability and proinflammatory cytokine of weanling pigsCas.zju: Source
- A multi-component herbal preparation, STW 5, shows anti-apoptotic effects in radiation induced intestinal mucositis in ratsPubmed:25022208
- Elevation of HO-1 Expression Mitigates Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Restores Tight Junction Function in a Rat Liver Transplantation ModelPubMed: 26064429
- Early prediction of intestinal mucosal barrier function impairment by elevated serum procalcitonin in rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Pubmed:26804005
- Modulation of gut microbiota contributes to curcumin-mediated attenuation of hepatic steatosis in ratspubmed:28341485
- A DPP-IV-resistant glucagon-like peptide-2 dimer with enhanced activity against radiation-induced intestinal injurypubmed:28522195
- Serum Diamine Oxidase in Pseudoallergy in the Pediatric Populationpubmed:28804811
- Protective effect of aplysin on liver tissue and the gut microbiota in alcohol-fed ratspubmed:28622357
- Protective Effect of Aplysin Supplementation on Intestinal Permeability and Microbiota in Rats Treated with Ethanol and IronPubmed:29861488
- Pregnancy-associated diamine oxidase originates from extravillous trophoblasts and is decreased in early-onset preeclampsiaPubmed:29679053
- Postoperative symbiotic in patients with head and neck cancer: a double-blind randomised trialPubmed:29277158
- The effect of fucoidan on intestinal flora and intestinal barrier function in rats with breast cancerPubmed:29384543
- LOCALIZATION OF COPPER-CONTAINING AMINE OXIDASE ENZYMES IN THE BLOOD
- Effects of fecal microbiota transplantation and joint application of probiotics on rats with alcoholic liver disease
- Potent anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides extracted from Blidingia minima and their effect in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease
- Modulation of gut microbiota contributes to effects of intensive insulin therapy on intestinal morphological alteration in high-fat-diet-treated micePubmed: 31749050
- Liraglutide Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Rats Administered a High-Fat DietPubmed: 32149099
- HMGB1‐associated necroptosis and Kupffer cells M1 polarization underlies remote liver injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in ratsPubmed: 31961020
- The effect of Poria cocos ethanol extract on the intestinal barrier function and intestinal microbiota in mice with breast cancerPubmed: 33039631
- Fecal microbiota transplantation from patients with autoimmune encephalitis modulates Th17 response and relevant behaviors in micePubmed: 32821439
- Effects of fucoidan on tumor prevention and gut flora
- Design and development of novel fasudil derivatives as potent anti‐breast cancer agent that improves intestinal flora and intestinal barrier function in rats34587363
- Bovine lactoferricin ameliorates intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier lesions in colitis through NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathways
- Transplanted hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells alleviated small intestinal ischaemia–reperfusion injury via intrinsic and paracrine mechanisms in a rat model