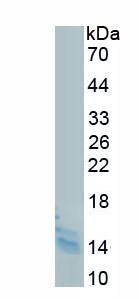
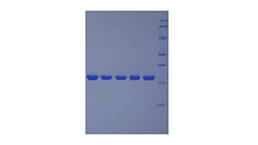
Active Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) 
ADHR; HYPF; HPDR2; PHPTC; Phosphatonin; Tumor-derived hypophosphatemia-inducing factor
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA746Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryCytokineTumor immunityInfection immunityGenetic science
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 80%
- Isoelectric Point7.2
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
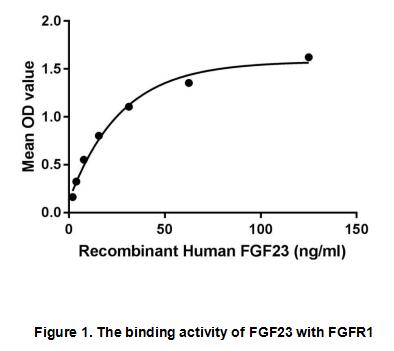
Fibroblast growth factor 23 or FGF23 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family which is responsible for phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. The main function of FGF23 seems to be regulation of phosphate concentration in plasma. FGF23 decreases the reabsorption and increases excretion of phosphate and suppress 1-alpha-hydroxylase, reducing its ability to activate vitamin D and subsequently impairing calcium absorption. Besides, Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1(FGFR1) has been identified as an interactor of FGF23, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human FGF23 and recombinant human FGFR1. Briefly, FGF23 were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100µl were then transferred to FGFR1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-FGF23 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of FGF23 and FGFR1 was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Usage
Reconstitute in ddH2O to a concentration of 0.1-0.25 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Prognostic impact of renal function in precapillary pulmonary hypertensionPubmed: 24011362
- FGF-23 associated with the progression of coronary artery calcification in hemodialysis patientsPubmed: 24180481
- Lower Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Levels in Young Adults With Crohn Disease as a Possible Secondary Compensatory Effect on the Disturbance of Bone and Mineral MetabolismPubmed: 23623649
- Prognostic impact of renal function in precapillary pulmonary hypertension.Pubmed:24011362
- Adverse effects of osteocytic constitutive activation of ?-catenin on bone strength and bone growthPubmed:25639729
- Fibroblast growth factor is associated to left ventricular mass index, anemia and low values of transferrin saturation El factor de crecimiento fibroblástico está asociado con el índice de masa ventricular izquierda, anemia y niveles bajos de saturación de la transferrinaPubMed: 26394828
- An Attempt to Evaluate Selected Aspects of “Bone–Fat Axis” Function in Healthy Individuals and Patients With Pancreatic CancerPubMed: 26266370
- Les biomarqueurs des calcifications vasculaires: quelles limites analytiques pour leur transfert de la recherche bioclinique à la pratique?PubMed: 26069069
- High-dose fast infusion of parenteral iron isomaltoside is efficacious in inflammatory bowel disease patients with iron-deficiency anaemia without profound changes in phosphate or fibroblast growth factor 23Pubmed:27326766
- Prostaglandin-E2 Mediated Increase in Calcium and Phosphate Excretion in a Mouse Model ofDistal Nephron Salt Wasting.pubmed:27442254
- Evaluation of concentration fibroblast growth factor FGF-23 in hemodialysed patients and after kidney transplantationpublication:312592751
- Associations between serum fibroblast growth factor 23 level and intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patientsissn:2394-2916
- ADAM17, a New Player in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder.pubmed:29056164
- Effect of cross-linked chitosan iron (III) on vascular calcification in uremic ratsPubmed:29763365
- Cerebrospinal fluid FGF23 levels correlate with a measure of impulsivityPubmed:29677623
- Serum and urine FGF23 and IGFBP-7 for the prediction of acute kidney injury in critically ill childrenPubmed:29907141
- Effect of Salt Intervention on Serum Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) in Chinese Adults: An Intervention StudyPubmed:29608553
- Disconnection of pulmonary and systemic arterial stiffness in COPDPubmed:29881265
- Prevalence of cardiac arrhythmia and risk factors in chronic kidney disease patientsPubmed:29970732
- High-serum phosphate and parathyroid hormone distinctly regulate bone loss and vascular calcification in experimental chronic kidney diseasePubmed: 30189026
- Alteration in serum concentrations of FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23 in patients with urothelial carcinomaPubmed: 30334297
- Altered Mineral Metabolism and Disequilibrium Between Calcification Promoters and Inhibitors in Chronic Hemodialysis PatientsPubmed: 30847765
- Evaluation of FGF‐23 and 25(OH)D3 levels in peri‐implant sulcus fluid in peri‐implant health and diseasesPubmed: 31407857
- PREVALANCE AND PROGRESSION OF CARDIOVASCULAR CALCIFICATIONS IN HAEMODIALYSIS PATIENTSPubmed: 28797410
- Serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels do not correlate with carotid intima-media thickness in patients with chronic kidney diseasePubmed: 31696838
- MiRNA-192-5p attenuates airway remodeling and autophagy in asthma by targeting MMP-16 and ATG7Pubmed: 31918268
- Is Serum FGF-23 Associated with Subclinic Atherosclerosis in Patients with AA Amyloidosis?
- THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTERIAL STIFNESS AND 25-(OH) VITAMIN D, FGF 23 IN MAINTENANCE HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS
- THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTERIAL STIFFNESS AND 25-(OH) VITAMIN D, FGF 23 IN MAINTENANCE HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS KRON?K ¡
- The Measurement and Interpretation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) ConcentrationsPubmed:35665817
- Genetic and clinical profile of patients with hypophosphatemic ricketsPubmed:35738466
- Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF 23) and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) as markers of mineral bone disease among Nigerians with non-diabetic kidney disease