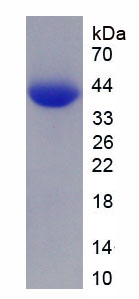
Active Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Specific Phospholipase D1 (GPLD1) 
GPIPLD; GPIPLDM; PIGPLD; PIGPLD1; Glycoprotein phospholipase D; Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D
- UOM
- FOB US$ 288.00 US$ 720.00 US$ 1,440.00 US$ 4,320.00 US$ 10,800.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APH975Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & Kinase
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point6.9
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
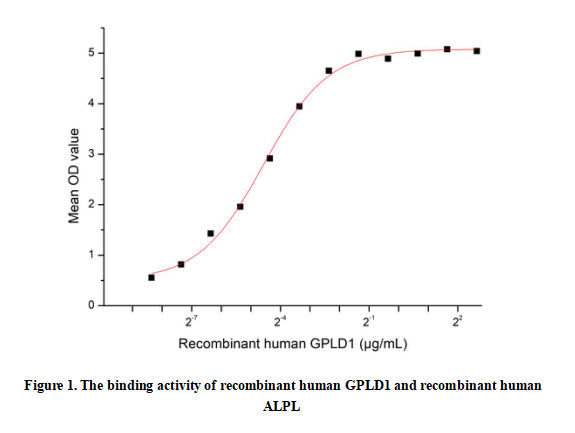
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Specific Phospholipase D1 (GPLD1) is a secreted enzyme that cleaves glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors, releasing GPI-anchored proteins from cell membranes into circulation. Primarily synthesized in the liver, it plays key roles in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and neurogenesis. GPLD1's activity modulates the bioavailability of important GPI-anchored proteins like alkaline phosphatase and folate receptors. Studies link elevated GPLD1 levels to metabolic disorders and aging-related cognitive decline, while its neuroprotective effects are being investigated. The enzyme's structure contains catalytic domains essential for hydrolyzing GPI linkages, making it a potential therapeutic target for metabolic and neurological diseases.Besides,Alkaline Phosphatase, Tissue-nonspecific (ALPL) has been identified as an interactor of GPLD1, thus a functional binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human GPLD1 and recombinant human ALPL. Briefly, GPLD1 was diluted serially in PBS with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 μl were then transferred to ALPL-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 1h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-GPLD1 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody for 1h at 37℃, wells were aspirated and washed 5 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50 µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450/630nm immediately. The binding activity of recombinant human GPLD1 and recombinant human ALPL was shown in Figure 1, the EC50 for this effect is 0.042µg/mL.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Plasma glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase D (GPI-PLD) and abdominal aortic aneurysmPubMed: PMC3443889
- Serum glypican4 and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D levels are associated with adipose tissue insulin resistance in obese subjects with …Pubmed: 32816247