Active Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) 
CD107B; INDO; Indoleamine-Pyrrole 2,3 Dioxygenase
- UOM
- FOB US$ 300.00 US$ 750.00 US$ 1,500.00 US$ 4,500.00 US$ 11,250.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APB547Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryEnzyme & KinaseInfection immunity
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
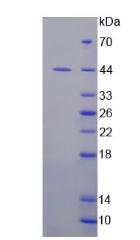
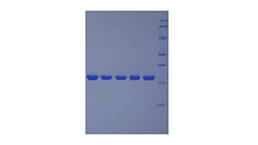
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point6.8
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test

IDO (Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1) is a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. Thus, bioactivity of recombinant human IDO was measured through its ability to oxidize L-tryptophan to N-formyl-kynurenine, using Methylene Blue as indicator. The reaction was performed in 50 mM MES, pH 6.5 (Assay Buffer), initiated by addition 50 μL of various concentrations of IDO (diluted by Assay Buffer) to 50 µL substrate mixture of 800 μM L-tryptophan, 9000 units/mL catalase (RPC418Hu05), and 40 μM Methyene Blue in assay buffer with equal volume of 80 mM ascorbic acid in 0.405 M Tris, pH 8.0. The final well serves as a negative control with no IDO, replaced with 50μL assay buffer. The absorbance was read in 321 nm in kinetic mode for 5 minutes. The result indicated that recombinant human IDO can oxidize L-tryptophan, the specific activity is 10581 pmol/min/μg.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- CCL18 differentiates dendritic cells in tolerogenic cells able to prime regulatory T cells in healthy subjectsPubmed: 21803856
- Potential immunosuppressive function of plasma indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in patients with aGVHD after allo-HSCTWiley: source
- Secretion of Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase, an Immunomodulatory Substance, by Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem CellIregway: Source
- CD40 Gene Silencing Reduces the Progression of Experimental Lupus Nephritis Modulating Local Milieu and Systemic MechanismsPubMed: PMC3683035
- Human CD14+ CTLA-4+ regulatory dendritic cells suppress T-cell response by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4-dependent IL-10 and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase production in hepatocellular carcinomaPubmed: 23960017
- Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase elevated in tumor-initiating cells is suppressed by mitocansScienceDirect: S0891584913006345
- Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from lung tumors maintain their immuno-suppressive abilities after high-dose irradiationFrontiersin:Source
- Immunogenicity and escape mechanisms of allogeneic tendon-derived stem cellsPubmed:24813640
- The expression of dendritic cell subsets in severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is alteredPubmed:24947894
- Chronic hepatitis C virus infection triggers spontaneous differential expression of biosignatures associated with T cell exhaustion and apoptosis signaling in peripheral blood mononucleocytesPubmed:25577277
- Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Lung Tumors Maintain Their Immunosuppressive Abilities after High-Dose IrradiationPubMed: 26029659
- Insights into the use of adipose stem cells for clinical cell therapy: Novel culturing conditions and characterization of multipotency and immunogenic propertiesHandle: 10024
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Infected Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulate Immunity via Interferon Beta and Indoleamine-2, 3-Dioxygenasepubmed:27695127
- Exploring Amino Acid-Capped Nanoparticles for Selective Anti-Parasitic Action and Improved Host BiocompatibilityPubmed:29883557
- Mechanisms of Leptin and Ghrelin Action on Maturation and Functions of Dendritic Cells
- Cognitive Decline, Cerebral-Spleen Tryptophan Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Regulation of the Txnip Gene in 3xTg-AD MicePubmed: 30980800
- Interaction of the immune-inflammatory and the kynurenine pathways in rats resistant to antidepressant treatment in model of depressionPubmed: 31176083
- Richard Schäfer,* Gabriele Spohn, Marco Bechtel, 2 Denisa Bojkova, 2 Patrick C. Baer, 3 Selim Kuçi, 4
- Altered Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase Production and Its Association to Inflammatory Cytokines in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Culture of Type 2 Diabetes?¡33343199
- Richard Sch?fer,* Gabriele Spohn, Marco Bechtel, 2 Denisa Bojkova, 2 Patrick C. Baer, 3 Selim Ku?i, 4
- Associations between expression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase enzyme and inflammatory cytokines in patients with first-episode drug-naive …34802039