Active Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein (LBP) 
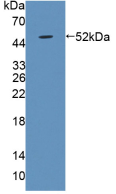
LPS-Binding Protein
- UOM
- FOB US$ 211.00 US$ 528.00 US$ 1,056.00 US$ 3,168.00 US$ 7,920.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APB406Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryInfection immunity
- Buffer Formulation20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point6.4
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
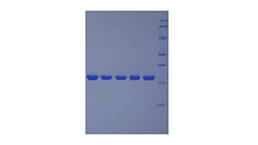
Activity test

Figure. The binding activity of LBP with CD14.
Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein (LBP) is a soluble acute-phase protein that binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (or LPS) to elicit immune responses by presenting the LPS to important cell surface pattern recognition receptors called CD14 and TLR4. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the acute-phase immunologic response to gram-negative bacterial infections. This protein is part of a family of structurally and functionally related proteins, including BPI, plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), and phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP). Besides, Cluster Of Differentiation 14 (CD14) has been identified as an interactor of LBP, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human LBP and recombinant human CD14. Briefly, LBP were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100µL were then transferred to CD14-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-LBP pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of LBP and CD14 was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Usage
Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl (pH8.0) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- A Marker of Endotoxemia Is Associated With Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders in Apparently Healthy ChineseDiabetes: source
- Oral serum-derived bovine immunoglobulin improves duodenal immune reconstitution and absorption function in patients with HIV enteropathyPubMed: PMC3754419
- Gut microbiome composition is linked to whole grain-induced immunological improvementsPubmed: 23038174
- High ambient temperature alleviates the inflammatory response and growth depression in pigs challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharidePubmed: 24792207
- The effect of normovolemic modified ultrafiltration on inflammatory mediators, endotoxins, terminal complement complexes and clinical outcome in high-risk cardiac surgery patientsPubmed: 23429100
- A gut microbiota-targeted dietary intervention for amelioration of chronic inflammation underlying metabolic syndrome.Pubmed: 24117923
- Frequency and Severity of Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy and Its Possible Relationship with Bacterial EndotoxemiaPubmed: 23907333
- Circulating pathogen associated molecular pattern – Binding proteins and High Mobility Group Box protein 1 in nascent metabolic syndrome: Implications for cellular Toll-like receptor activityPubmed:25063948
- Identification of plasma protein markers common to patients with malignant tumour and Abnormal Savda in Uighur medicine: a prospective clinical studyPubmed:25652121
- Increased adipose tissue secretion of Fetuin-A, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and high-mobility group box protein 1 in metabolic syndromePubMed: 25978344
- Systemic levels of human β-defensin 1 are elevated in patients with cirrhosisPubMed: 26751578
- Comparative proteomics of milk fat globule membrane in goat colostrum and mature milkPubmed:27173528
- High serum lipopolysaccharide binding protein is associated with increased mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosispubmed:27712029
- Modulation of gut microbiota and gut-generated metabolites by bitter melon results in improvement in the metabolic status in high fat diet-induced obese rats10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.050
- Adamdec1, Ednrb and Ptgs1/Cox1, inflammation genes upregulated in the intestinal mucosa of obese rats, are downregulated by three probiotic strains.pubmed:28512356
- A standardized extract of the fruit of Hovenia dulcis alleviated alcohol-induced hangover in healthy subjects with heterozygous ALDH2: A randomized, controlled, crossover trial.pubmed:28750942
- On a Western diet, APOE ɛ4 is associated with low innate immune sensing, but not APOE ɛ3Pubmed:29928926
- Influence of yeast culture and feed antibiotics on ruminal fermentation and site and extent of digestion in beef heifers fed high grain rationsPubmed:30060086
- Using ruminally protected and nonprotected active dried yeast as alternatives to antibiotics in finishing beef steers: growth performance, carcass traits, blood …Pubmed: 30184125
- Evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 on biomarkers of inflammation, cardiovascular risk and liver steatosis in obese adults with metabolic …Pubmed: 30453950
- Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways
- High-dose Glycerol Monolaurate Up-Regulated Beneficial Indigenous Microbiota without Inducing Metabolic Dysfunction and Systemic Inflammation: New Insights …
- Ruminally protected and unprotected Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation products as alternatives to antibiotics in finishing beef steersPubmed: 31410465
- Lactobacillus reuteri V3401 Reduces Inflammatory Biomarkers and Modifies the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: The PROSIR StudyPubmed: 31370223
- Effects of sinomenine in LPS‐associated diseases are related to inhibition of LBP, Mac‐1, and L‐selectin levelsPubmed: 31490576
- Needle-shaped amyloid deposition in rat mammary gland: evidence of a novel amyloid fibril proteinPubmed: 31615282
- Ethanol Extract of Propolis Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Obesity in Association with Modulation of Gut Microbiota in MicePubmed: 32156386
- Gut microbiota from coronary artery disease patients contributes to vascular dysfunction in mice by regulating bile acid metabolism and immune activationPubmed: 33036625
- Oxidation of fish oil exacerbates alcoholic liver disease by enhancing intestinal dysbiosis in micePubmed: 32879433
- Antibiotic Treatment Reduces the Health Benefits of Soy ProteinPubmed: 32729948
- Highly Branched RG-I Domain Enrichment are Indispensable for Pectin Mitigating Against High-Fat Diet-Induced ObesityPubmed: 32633953
- Molecular characterization and expression analysis of chemokine (CXCL12) from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)Pubmed: 32540504
- Tandem Mass Tag (TMT)-based quantitative proteomics reveals potential targets associated with onset of Sub-clinical Mastitis in cowsPubmed: 32518370
- Corneal epithelial injury-induced norepinephrine promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitisPubmed: 32376471
- Naringin Attenuates High Fat Diet Induced Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Gut Bacterial Dysbiosis in Mice
- Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) for inflammatory regulation after excision and grafting of severe burn wounds in rats33313794
- Processing Index of Barley Grain and Dietary Undigested Neutral Detergent Fiber Concentration Affected Chewing Behavior, Ruminal pH and Total Tract Nutrient?¡33474564
- Influence of a Biotechnologically Produced Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus sajor-caju) on the Gut Microbiota and Microbial Metabolites in Obese Zucker Rats33497213
- Melatonin alleviates Ochratoxin A-induced liver inflammation involved intestinal microbiota homeostasis and intestinal microbiota-independent manner33582472
- Studies on Mastitis Caused by Translocated-Bacterial Components in Ruminants
- Monocyte transcriptomes from patients with axial spondyloarthritis reveal dysregulated monocytopoiesis and a distinct inflammatory imprint34560894
- Composition and Functions of the Gut Microbiome in Pediatric Obesity: Relationships with Markers of Insulin Resistance34361925
- The Prebiotic Potential of Geraniin and Geraniin-Enriched Extract against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Sprague Dawley RatsPubmed:35453317
- Elucidating the role of the gut microbiota in the physiological effects of dietary fiberPubmed:35562794
- Local free fatty acids trigger the expression of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in murine white adipose tissuePubmed:35433160
- Сorrelation between the level of 25 (OH) D3 in blood, the content of antimicrobial peptides in oral fluid and dental caries intensity in young individuals