Active Platelet Derived Growth Factor Subunit B (PDGFB) 
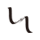
PDGF-B; PDGF2; SIS; SSV; C-sis; Simian Sarcoma Viral(v-sis)Oncogene Homolog; Platelet Derived Growth Factor Beta Polypeptide; Proto-oncogene c-Sis; Becaplermin
- UOM
- FOB US$ 331.00 US$ 828.00 US$ 1,656.00 US$ 4,968.00 US$ 12,420.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APC921Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryCytokine
- Buffer Formulation20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
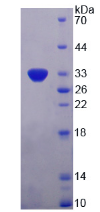
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point9.5
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
Figure. The binding activity of PDGFB with NRP-1.
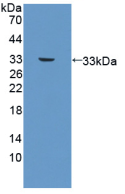
Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B (PDGFB) is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family in humans. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha (PDGFA) polypeptide (PDGF-AB), where the dimers are connected by disulfide bonds. Besides, Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) has been identified as an interactor of PDGFB, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human PDGFB and recombinant human NRP-1. Briefly, PDGFB were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100uL were then transferred to NRP-1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti- PDGFB pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of PDGFB and NRP-1 was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.

Figure. Cell proliferation of MCF-7 cells after stimulated with IGF2.
PDGFs are mitogenic during early developmental stages, driving the proliferation of undifferentiated mesenchyme and some progenitor populations. During later maturation stages, PDGF signalling has been implicated in tissue remodelling and cellular differentiation, and in inductive events involved in patterning and morphogenesis. In addition to driving mesenchymal proliferation, PDGFs have been shown to direct the migration, differentiation and function of a variety of specialised mesenchymal and migratory cell types, both during development and in the adult animal. A proliferation assay was conducted to detect the bioactivity of recombinant human PDFGB using MCF-7 cells. Briefly, MCF-7 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 5,000 cells/well and allowed to attach, replaced with serum-free overnight, then the medium was replaced with 1% serum standard DMEM prior to the addition of various concentrations of PDGFB. After incubated for 96h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10µL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37℃. Proliferation of MCF-7 cells after incubation with PDGFB for 96h observed by inverted microscope was shown in Figure 2. Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8 ) assay after incubation with recombinant PDGFB for 96h. The result was shown in Figure 3. It was obvious that PDGFB significantly increased cell viability of MCF-7 cells.
(A) MCF-7 cells cultured in DMEM, stimulated with 1ng/mL PDGFB for 96h;
(B) Unstimulated MCF7 cells cultured in DMEM for 96h.
Usage
Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl (pH8.0) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Inhibition of Glomerular Mesangial Cell Proliferation by siPDGF-B-and siPDGFR-β-Containing Chitosan Nanoplexespubmed:27975193
- In vitro PDGF-B gene silencing studies and In vivo delivery of siRNA to the rat kidney using Chitosan/siRNA nanoplexes5000184338
- Platelet-derived growth factor and stromal cell-derived factor-1 promote the skin wound repairing effect of bone mesenchymal stem cells: a key role of matrix metalloproteinase 1 and collagensISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058424
- Melatonin promotes osteoblastic differentiation and regulates PDGF/AKT signaling pathwayPubmed: 31535749
- PDGF-BB homodimer serum level–a good indicator of the severity of alcoholic liver cirrhosisPubmed: 32208584
- Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in tissue-engineered bladders33868627