Active Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2) 
CD309; FLK1; VEGFR; KDR; A Type III Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; Kinase Insert Domain Receptor; Kinase Insert Domain Receptor; Fetal Liver Kinase-1
- UOM
- FOB US$ 216.00 US$ 540.00 US$ 1,080.00 US$ 3,240.00 US$ 8,100.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APB367Hu61
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategorySignal transductionCD & Adhesion moleculeTumor immunity
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point6.5
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
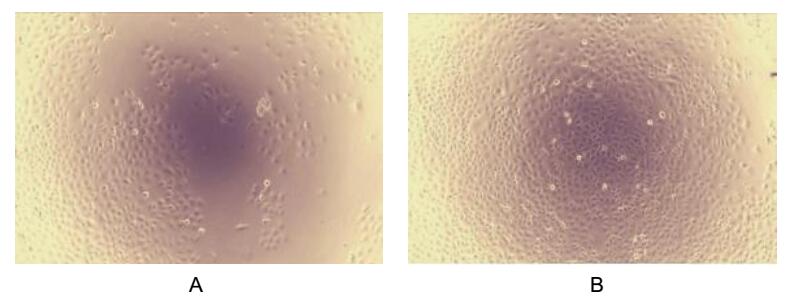
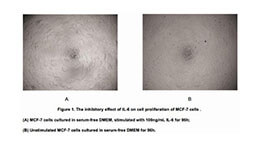
Figure. Cell proliferation of ECV-304 cells inhibit by VEGFR2.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2) also known as kinase insert domain receptor acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. VEGFR2 functions as the primary mediator of vascular endothelial growth factor activation in endothelial cells. Regulation of VEGFR-2 expression appears critical in mitogenesis, differentiation, and angiogenesis. To test the effect on inhibit the VEGF-dependent proliferation of endothelium cells, ECV-304 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 5,000 cells/well and allowed to attach, replaced with serum-free overnight, then the medium was replaced with 2% serum standard DMEM including 1μg/mL Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C (VEGFC) and various concentrations of recombinant human VEGFR2. After incubated for 96h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10µL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37℃. Proliferation of ECV-304 cells after incubation with VEGFR2 for 96h observed by inverted microscope was shown in Figure 1. Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8) assay after incubation with recombinant VEGFR2 for 96h. The result was shown in Figure 2. It was obvious that VEGFR2 significantly inhibit cell viability of ECV-304.
(A) ECV-304 cells cultured in DMEM, stimulated with 10ng/mL VEGFR2 for 96h;
(B) Unstimulated ECV-304 cells cultured in DMEM for 96h.
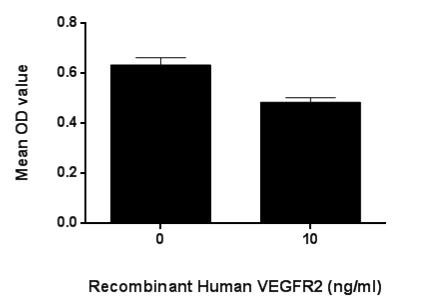
Figure. VEGFR2 inhibit VEGF-dependent proliferation of ECV-304 cells.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Peritumoral brain edema in angiomatous supratentorial meningiomas: an investigation of the vascular endothelial growth factor A pathwayPubMed: 23398358
- Antioxidant and bone repair properties of quercetin-functionalized hydroxyapatite: an in vitro osteoblast-osteoclast-endothelial cell co-culture studyPubMed: 26689470
- Antioxidant and bone repair properties of quercetin-functionalized hydroxyapatite: An in vitro osteoblast–osteoclast–endothelial cell co-culture studyPubmed:26689470
- A Human 3D In Vitro Model to Assess the Relationship Between Osteoporosis and Disseminationto Bone of Breast Cancer Tumor Cells.pubmed:27925188
- The directional migration and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells toward vascular endothelial cells stimulated by biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic10.1093/rb/rbx028
- VEGF-R2 and TNF-R1 expression and cytokine production by samples of mammary adenocarcinomas and correlations with histopathological parameters of these …Pubmed:29985074
- Effect of isotretinoin (13-cis-retinoic acid) on levels of soluble VEGF receptors (sVEGFR1, sVEGFR2, sVEGFR3) in patients with acne vulgarisPubmed: 32043381
- Encapsulated VEGF 121-PLA microparticles promote angiogenesis in human endometrium stromal cells33523322
- Intuitive repositioning of an anti-depressant drug in combination with tivozanib: precision medicine for breast cancer therapy34324118
- Effect of subacute poisoning with lambdacyhalothrin on vascular endothelial growth factor 2 receptor in mice kidneysPubmed:35643467