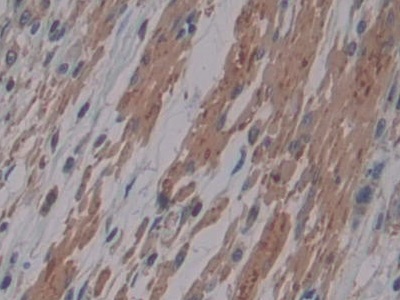
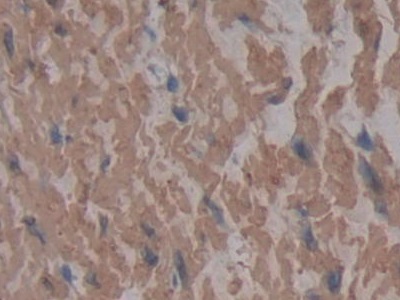
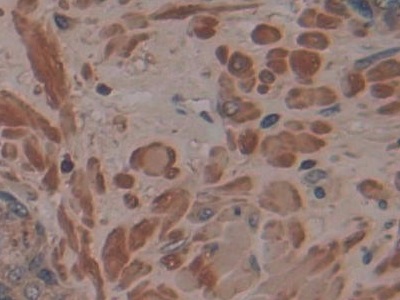
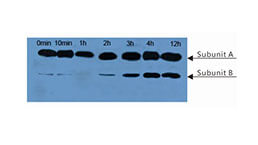
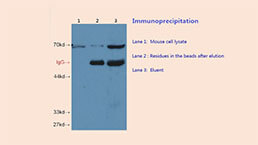
Monoclonal Antibody to Cross Linked N-Telopeptide Of Type I Collagen (NTXI) 
NTX-I; NTX1
- UOM
- FOB US$ 171.00 US$ 398.00 US$ 569.00 US$ 1,423.00 US$ 5,690.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.MAA639Hu24
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsIHC
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayBone metabolism
- SourceMonoclonal antibody preparation, Host Mouse
- Ig Isotype IgG2a Kappa, Clone Number A9
- PurificationProtein A + Protein G affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen CPA639Hu21-OVA Conjugated Cross Linked N-Telopeptide Of Type I Collagen (NTXI)
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 0.5mg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against NTXI. It has been selected for its ability to recognize NTXI in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Immunohistochemistry: 5-30µg/mL;
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Dyslipidemic high-fat diet affects adversely bone metabolism in mice associated with impaired antioxidant capacityScienceDirect: S0899900709004717
- Differential mRNA expression profiles in proximal tibia of aged rats in response to ovariectomy and low-Ca dietScienceDirect: S875632820800776X
- Promotion of bone formation by naringin in a titanium particle‐induced diabetic murine calvarial osteolysis modelWiley: Source
- A Mediterranean Diet Enriched with Olive Oil Is Associated with Higher Serum Total Osteocalcin Levels in Elderly Men at High Cardiovascular RiskPubMed: PMC3462931
- Biochemical markers of bone resorption are present in human milk: implications for maternal and neonatal bone metabolismPubmed:25109232
- An NMR Metabolomic Study on the Effect of Alendronate in Ovariectomized MicePubmed:25184758
- Strontium Ranelate Reduces the Fracture Incidence in a Growing Mouse Model of Osteogenesis ImperfectaPubMed: 26679066
- Comparative effects of brown and golden flaxseeds on body composition, inflammation and bone remodelling biomarkers in perimenopausal overweight womenS1756464617301561
- Impact of a chronic smoking habit on the osteo-immunoinflammatory mediators in the peri-implant fluid of clinically healthy dental implants.pubmed:27328151
- Impact of a triclosan‐containing toothpaste during the progression of experimental peri‐implant mucositis: Clinical parameters and local pattern of osteo …Pubmed:29520826
- Triclosan‐containing fluoride toothpaste on clinical parameters and osteo‐inflammatory mediators when applied in a stent during experimental peri‐implant mucositis …Pubmed: 30659666
- AAV-anti-miR-214 prevents collapse of the femoral head in osteonecrosis by regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activitiesPubmed: 31739209
- Material-Dependent Formation and Degradation of Bone Matrix—Comparison of Two CryogelsPubmed: 32517006
- Comparable Effects of Strontium Ranelate and Alendronate Treatment on Fracture Reduction in a Mouse Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta33506016
- Effects of icariin on the fracture healing in young and old rats and its mechanism34511043
- Gujiansan Ameliorates Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head by Regulating Autophagy via the HIF-1α/BNIP3 Pathway34512780