ELISA Kit for Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) 
- UOM
- FOB US$ 560.00 US$ 800.00 US$ 3,600.00 US$ 6,800.00 US$ 56,000.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.AEA546Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsEnzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antibody Detection.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryInfection immunityImmune moleculeHematologyPulmonology
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 98-105 | 101 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 84-95 | 87 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 85-94 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 89-101% | 79-92% | 83-98% | 88-102% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 83-101% | 92-101% | 92-105% | 96-104% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 98-105% | 95-104% | 81-95% | 78-89% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
5. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
6. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.

Test principle
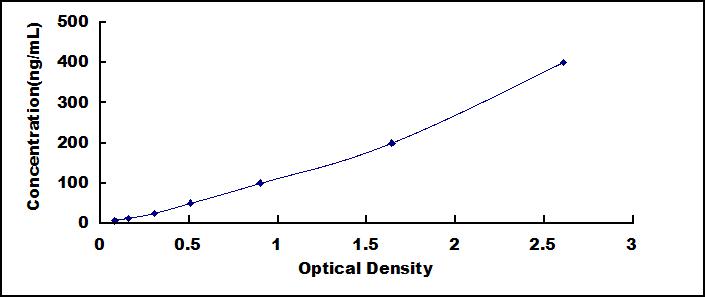
The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antigen. Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with a Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody. After TMB substrate solution is added, those wells that contain Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) will exhibit a change in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by the addition of sulphuric acid solution and the color change is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450nm ± 10nm. The concentration of Anti-Immunoglobulin A Antibody (Anti-IgA) in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Sequence-Based Typing-Study on the Relationship Between Subclinical Mastitis and BoLA-DRB3.2* Allelic Polymorphism in Egyptian CowsIdosi: Source
- EVALUATION OF PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF COLOSTRUM SUPPLEMENTED DAHIIjfans: Source
- Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth performance, immune function, and cecal microflora in broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli K88Pubmed: 24570422
- Specific humoral immune response induced by Propionibacterium acnes can prevent Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in miceAsm: Source
- Speci?c Humoral Immune Response Induced by Propionibacterium acnes Can Prevent Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Infection in MicePubmed:24429068
- Proteomics on porcine haptoglobin and IgG/IgA show protein species distribution and glycosylation pattern to remain similar in PCV2-SD infectionPubmed:24576640
- Dietary squid ink polysaccharide could enhance SIgA secretion in chemotherapeutic micePubmed:25308407
- Oropharyngeal colostrum administration in extremely premature infants: an RCT.Pubmed:25624376
- Fecal microbiota transplantation and bacterial consortium transplantation have comparable effects on the re-establishment of mucosal barrier function in mice with intestinal dysbiosisPubMed: 26217323
- Effects of fermented cottonseed meal on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, immune functions, antioxidative abilities, and cecal microflora in broilers10.108:09540105.2017.1311308
- SYSTEMISCHE ENTZÜNDUNG BEI CHRONISCHER NIERENINSUFFIZIENZ – DIE ROLLE DER DARMFLORApatent:US9763998B2
- Sub-chronic inhalation of reclaimed water-induced fibrotic lesion in a mouse modelPubmed:29655095
- Recombinant Lactococcus lactis co-expressing OmpH of an M cell-targeting ligand and IBDV-VP2 protein provide immunological protection in chickensPubmed:29289381
- Effects of and on growth performance, immune function and volatile fatty acid level of caecal digesta in broilers10.1080:09540105.2018.1457013
- Effect of Multi-Microbial Probiotic Formulation Bokashi on Pro-and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Profile in the Serum, Colostrum and Milk of Sows, and in a …Pubmed:29305686
- Altered immunoglobulins (A and G) in Ghanaian patients with type 2 diabetesPubmed:29623201
- The gut flora modulates intestinal barrier integrity but not progression of chronic kidney disease in hyperoxaluria-related nephrocalcinosisPubmed: 31081025
- Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius): Effect on Integrity of Intestinal Barrier, Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in Animal Model of Colon Cancer (P06-052-19)Pubmed: 31225040
- Effects of Paramylon Extracted from Euglena gracilis EOD-1 on Parameters Related to Metabolic Syndrome in Diet-Induced Obese MicePubmed: 31330894
- Effects of polysaccharides from Yingshan Yunwu tea on meat quality, immune status and intestinal microflora in chickensPubmed: 32224178
- Effect Long-Term Exposure to Different Doses of Lipopolysaccharides on the Intestinal Mucosal Immune Barrier
- Effects of chitooligosaccharide supplementation on laying performance, egg quality, blood biochemistry, antioxidant capacity and immunity of laying hens during the …
- Women Scientist Scientist Mentor
- MicroRNA profiling in Chinese children with Henoch©\Schonlein purpura and association between selected microRNAs and inflammatory biomarkers33533510
- Trace endotoxin in reclaimed water is only one of the risk sources in subchronic inhalation exposure34090073
- Monascus ruber fermented Panax ginseng ameliorates lipid metabolism disorders and modulate gut microbiota in rats fed a high-fat diet34098018
- Dietary Supplementation of Inulin Ameliorates Subclinical Mastitis via Regulation of Rumen Microbial Community and Metabolites in Dairy Cows34494854
- Sulfated modification enhances the immunomodulatory effect of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharide on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice through …34865774
- Three Urban of China: A Cohort Study of Maternal-Infant Factors and HM Protein ComponentsPubmed:35438093
- The effect of the multi-strain probiotic preparation EM Bokashi® on selected parameters of the cellular immune response in pigs
- Bovine lactoferricin ameliorates intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier lesions in colitis through NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathways
- Salivary IgA Depression in Drug-Influenced Gingival Enlargement among Hypertensive Patients