Laryngeal Paralysis (LP)
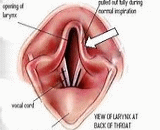
Laryngeal paralysis in animals is a condition in which the nerves and muscles that control the movements of one or both arytenoid cartilages of the larynx cease to function, and instead of opening during inspiration and closing during swallowing, the arytenoids remain stationary in a somewhat neutral position. Specifically, the muscle that causes abduction of the arytenoid cartilage, the cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle, ceases to function. This leads to inadequate ventilation during exercise and during thermoregulatory panting as well as incomplete protection of the airway during swallowing.
Organism species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
- Disease model DSI660Mu01 Mouse Model for Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- Disease model DSI660Ra01 Rat Model for Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Cavia (Guinea pig )
- Disease model DSI660Gu01 Cavia Model for Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Disease model DSI660Rb01 Rabbit Model for Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer
Organism species: Canis familiaris; Canine (Dog)
- Disease model DSI660Ca01 Canine Model for Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) In Stock
- Customized Service n/a Tissue of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Tissue Customized Service Offer
- Customized Service n/a Serums of Laryngeal Paralysis (LP) (If Necessary) Serums Customized Service Offer


