Active Calmodulin (CAM) 
CALcium MODULated ProteIN
- UOM
- FOB US$ 268.00 US$ 670.00 US$ 1,340.00 US$ 4,020.00 US$ 10,050.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APA640Hu61
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategorySignal transductionMetabolic pathwayApoptosisInfection immunity
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
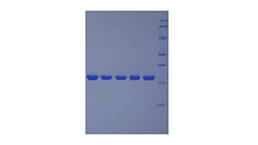
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 95%
- Isoelectric Point3.8
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
Activity test
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
Citations
- Identification of Novel Translational Urinary Biomarkers for Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury Using Proteomic Profiling in MicePubMed: PMC3498140
- Role of Calmodulin-Calmodulin Kinase II, cAMP/Protein Kinase A and ERK 1/2 on Aeromonas hydrophila-Induced Apoptosis of Head Kidney MacrophagesPubmed:24763432
- Calcium and Superoxide-Mediated Pathways Converge to Induce Nitric Oxide-Dependent Apoptosis in Mycobacterium fortuitum-Infected Fish MacrophagesPubmed:26752289