Active Surfactant Associated Protein D (SPD) 
SFTPD; COLEC7; PSP-D; SFTP4; SP-D; Pulmonary Surfactant Protein D; Collectin-7; Lung surfactant protein D
- UOM
- FOB US$ 328.00 US$ 821.00 US$ 1,642.00 US$ 4,926.00 US$ 12,315.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.APB039Ra61
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryInfection immunityPulmonology
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 5% Trehalose.
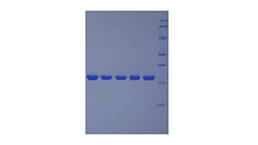
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point7.7
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Activity test
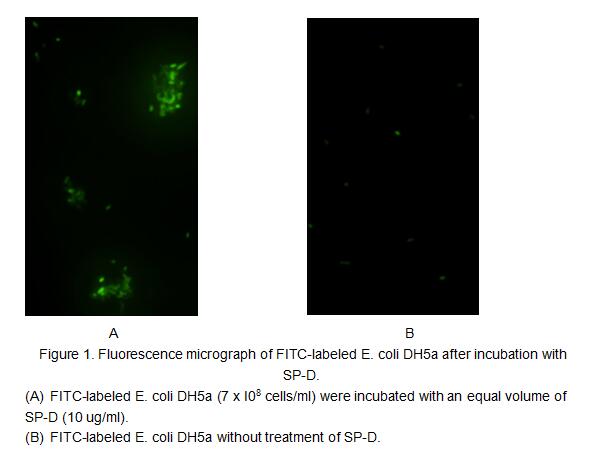
SP-D (surfactant protein-D) is a 43 kDa member of the collectin family of innate immune modulators. It is constitutively secreted by alveolar lining cells and epithelium associated with tubular structures. Its principal components consist of a collagen-like region and a C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD), a structure that further places it in a subset of an expanded group of proteins termed defense collagens. SP-D is known to bind both SIRP alpha and the calreticulin/CD91 complex on macrophages. When the ratio of antigen/pathogen to available CRDs is low, antigen can be bound without occupying all available CRDs. The free CRDs will bind to SIRP alpha, generating a signal that downmodulates the inflammatory response. When virtually all CRDs are occupied by ligand, however, free CRDs are not available for SIRP alpha binding. The activity of the recombinant rat SPD was measured by its ability to bind fluorescein-conjugated E. coli bioparticles. The rrSPD was diluted to 10 ug/ml in assay buffer of 20 mM Tris, 137 mM NaCl, 1 mM CaC12, pH7.4 and fluorescein-conjugated E. coli was diluted to 7*108 cells/ml. Equal volume of 10 ug/ml rrSPD and fluorescein-conjugated E. coli were mixed and incubated at room temperature for 1h. 10 ul mixture was took onto the slide and observed under the fluorescence microscopy. The result was shown in figure 1, the rrSPD could bind fluorescein-conjugated E. coli bioparticles.
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Surfactant protein A and D in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis and corticosteroid responseIngenta: art00005
- Evaluation of acute oxidative stress induced by NiO nanoparticles in vivo and in vitroPubMed: 21233593
- Comparison of acute oxidative stress on rat lung induced by nano and fine-scale, soluble and insoluble metal oxide particles: NiO and TiO2PubMed: 22642288
- Detection of surfactant proteins A, B, C, and D in human nasal mucosa and their regulation in chronic rhinosinusitis with polypsPubMed: 23406594
- Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Express and Secrete Human Surfactant ProteinsPubMed: PMC3551896
- The Detection of Surfactant Proteins A, B, C and D in the Human Brain and Their Regulation in Cerebral Infarction, Autoimmune Conditions and Infections of the CNSPubMed: PMC3787032
- Nachweis und Charakterisierung des Oberfl?chenproteins PLUNC (Palate, Lung and Nasal Clone Protein) an der Augenoberfl?che und Bedeutung für das Trockene AugeOpus4:Source
- The Cerebral Surfactant System and Its Alteration in HydrocephalicConditions.pubmed:27656877
- Correlations of Ventricular Enlargement with Rheologically Active SurfactantProteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid.pubmed:28101052
- Chronic lung injury and impaired pulmonary function in a mouse model of acid ceramidase deficiency.pubmed:29167126
- Rheologically Essential Surfactant Proteins of the CSF Interacting with Periventricular White Matter Changes in Hydrocephalus Patients–Implications for CSF …Doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01648-z
- Elevated plasma levels of epithelial and endothelial cell markers in COVID-19 survivors with reduced lung diffusing capacity six months after hospital …Pubmed:35189887
- The association between sPD-1 levels versus liver biochemistry and viral markers in chronic hepatitis B patients: a comparative study of different sPD-1 …Pubmed:35361235