Eukaryotic Cathepsin D (CTSD) 
CPSD; CLN10; Lysosomal Aspartyl Protease; Ceroid-Lipofuscinosis,Neuronal 10
- UOM
- FOB US$ 246.00 US$ 615.00 US$ 1,230.00 US$ 3,690.00 US$ 9,225.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.EPB280Hu61
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
-
Applications
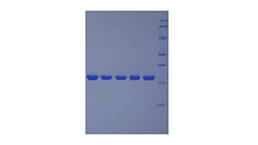
Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB.
If bio-activity of the protein is needed, please check active protein.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunity
- Source Eukaryotic expression, Host 293F cell
- Endotoxin Level<1.0EU per 1µg (determined by the LAL method)
- Subcellular LocationSecreted
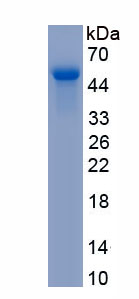
- Molecular Mass 44.2kDa, Accurate 48kDa(Analysis of differences refer to the manual)
- Residues & TagsLeu21~Leu412 with N-terminal His Tag
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point6.5
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
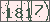
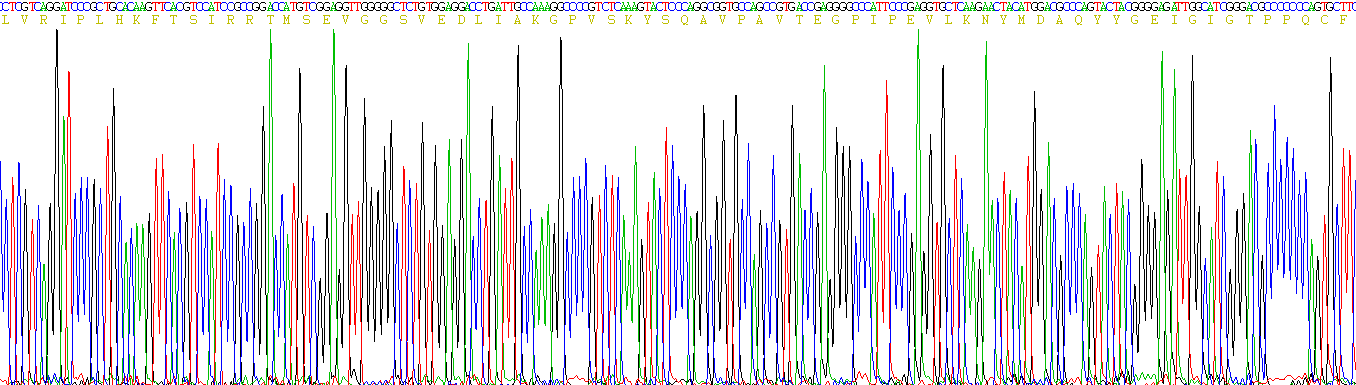
Sequence
Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Protein Labeling Customized Service
Protein Labeling Customized Service
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Cathepsin D is released after severe tissue trauma in vivo and is capable of generating C5a in vitroScienceDirect: S0161589011008297
- Plasma Cathepsin D Levels: A Novel Tool to Predict Pediatric Hepatic InflammationPubMed: 25732418
- Plasma cathepsin D correlates with histological classifications of fatty liver disease in adults and responds to interventionpubmed:27922112
- Berberine ameliorates intrahippocampal kainate-induced status epilepticus and consequent epileptogenic process in the rat: Underlying mechanismspubmed:28061403
- Limited applicability of cathepsin D for the diagnosis and monitoring of non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis
- Plasma cathepsin D activity is negatively associated with hepatic insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese humansPubmed: 31690989
- Iron and Advanced Glycation End Products: Emerging Role of Iron in Androgen Deficiency in ObesityPubmed: 32235809
- LVV-hemorphin-7 (LVV-H7) plays a role in antinociception in a rat model of alcohol-induced pain disorders33253777
- Identification of Cathepsin D as a Plasma Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease33445607
- Analysis of silymarin-modulating effects against acrylamide-induced cerebellar damage in male rats: Biochemical and pathological markers33965515
- PGRS Domain of Rv0297 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is Involved in Modulation of Macrophage Functions to Favor Bacterial Persistence33042856
- Serum CathepsinD in pregnancy: relation with metabolic and inflammatory markers and effects of fish oils and probioticsPubmed:35304048
- A Comparison of Various Chips Used for the Manufacture of Biosensors Applied in Non-Fluidic Array SPRi, Based on the Example of Determination of Cathepsin DPubmed:35049649