Recombinant Procollagen II C-Terminal Propeptide (PIICP) 
P2CP; C-Propeptide Of Type II Procollagen; Procollagen II Carboxy Terminal Propeptide
- UOM
- FOB US$ 232.00 US$ 580.00 US$ 1,160.00 US$ 3,480.00 US$ 8,700.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.RPA964Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
-
Applications
Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB.
If bio-activity of the protein is needed, please check active protein.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryInfection immunityBone metabolismRheumatology
- Source Prokaryotic expression, Host E.coli
- Endotoxin Level<1.0EU per 1µg (determined by the LAL method)
- Subcellular LocationSecreted
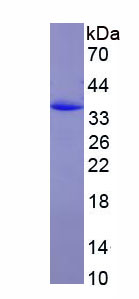
- Molecular Mass 31.2kDa, Accurate 35kDa(Analysis of differences refer to the manual)
- Residues & TagsAsp1242~Leu1487 with N-terminal His Tag
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 90%
- Isoelectric Point6.5
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
Sequence

Usage
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 TBST Buffer
TBST Buffer
-
 TBS Buffer
TBS Buffer
-
 TRIS Buffer
TRIS Buffer
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Evaluation of the effect of N-acetyl-glucosamine administration on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals without symptoms of arthritis: A …10.3892
- Evaluation of the effect of administering N-acetyl-glucosamine-containing green tea supplement on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals without symptoms of arthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study309
- Effect of N-acetylglucosamine administration on cartilage metabolism and safety in healthy subjects without symptoms of arthritis: A case reportpubmed:28413518
- Evaluation of the effect of salmon nasal proteoglycan on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in individuals with knee joint discomfort: A randomized double‑blind placebo‑controlled clinical studyetm:14
- Evaluation of the efficacy of Ajuga decumbens extract supplement in individuals with knee discomfort associated with physical activity: A randomized, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled study10.3892/etm.2017.5064
- Evaluation of the chondroprotective action of N‑acetylglucosamine in a rat experimental osteoarthritis pubmed:28912864
- Evaluation of the effect of N-acetyl-glucosamine administration on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical studyview/366
- No effects of hyperosmolar culture medium on tissue regeneration by human degenerated nucleus pulposus cells despite upregulation extracellular matrix genesfulltext:2018/03010
- Fibulin-3 and other cartilage metabolism biomarkers in relationship to calprotectin (MRP8/14) and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with …68362.pdf
- サケ鼻軟骨由来プロテオグリカン摂取による関節保護効果
- No Effects of Hyperosmolar Culture Medium on Tissue Regeneration by Human DegeneratedPubmed: 25856264
- Effectiveness of collagen supplementation on pain scores in healthy individuals with self-reported knee pain; A randomized controlled trialPubmed: 31990581
- Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Nucleus Pulposus RegenerationPubmed: 32295299
- Concerted Actions by PIICP, CTXII, and TNF-¦Á in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis33924892