Recombinant Syndecan 1 (SDC1) 
CD138; SDC; SYND1; Syndecan Proteoglycan 1
Overview
Properties
- Product No.RPB966Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
-
Applications
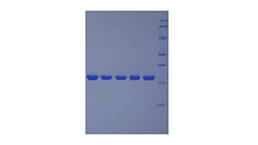
Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB.
If bio-activity of the protein is needed, please check active protein.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryTumor immunityInfection immunityImmunodeficiency
- Source Prokaryotic expression, Host E.coli
- Endotoxin Level<1.0EU per 1µg (determined by the LAL method)
- Subcellular LocationMembrane, Secreted
- Molecular Mass 56.2kDa, Accurate 75kDa(Analysis of differences refer to the manual)
- Residues & TagsGln23~Leu253 with N-terminal His and GST Tag
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder, Purity > 80%
- Isoelectric Point5.0
Share your citation
Upload your experimental result
Review
Leave a message
Loading...
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review
Please attach serial No. on instruction manual


Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Name*
Organization
Address
E-mail address*
Telephone
Inquiry*
Verification code*
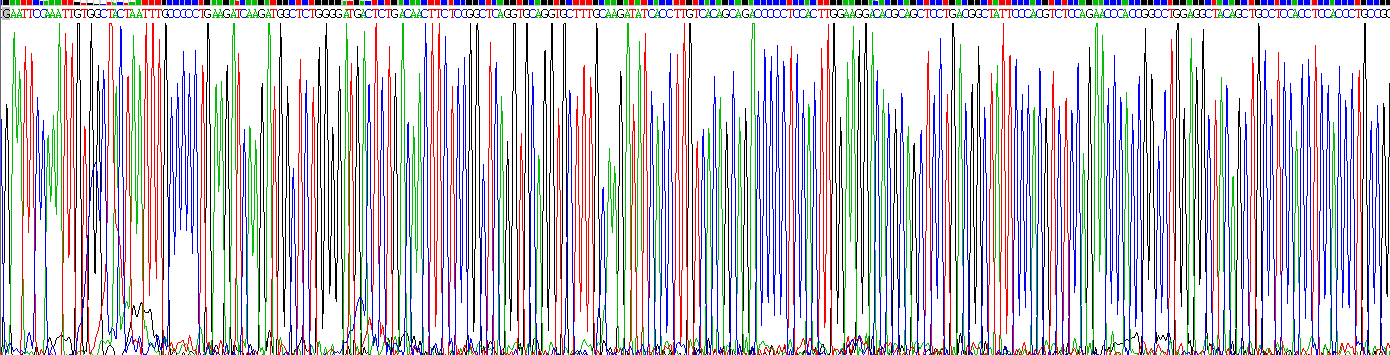
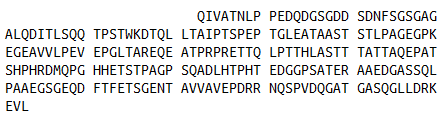
Sequence
Usage
Reconstitute in ddH2O to a concentration less than or equal to 0.1mg/mL. Do not vortex.
Storage
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Increment services
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit
Endotoxin Removal Kit
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Protein Labeling Customized Service
Protein Labeling Customized Service
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Recombinant Protein Customized Service
Recombinant Protein Customized Service
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Endotoxin Removal Kit II
Endotoxin Removal Kit II
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
Citations
- Increased level of soluble syndecan-1 in serum correlates with myocardial expression in a rat model of myocardial infarctionSpringerLink: a201w3l18k257462
- Sdc1 Overexpression Inhibits the p38 MAPK Pathway and Lessens Fibrotic Ventricular Remodeling in MI RatsSpringer: Source
- Damage of the endothelial glycocalyx in chronic kidney diseasePubmed:24727235
- Effect of valproic acid and injury on lesion size and endothelial glycocalyx shedding in a rodent model of isolated traumatic brain injuryPubmed:25058256
- Impairment of the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Cardiogenic Shock and its Prognostic RelevancePubmed:25692257
- Dexamethasone Suppressed LPS-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase and Its Effect on Endothelial Glycocalyx SheddingPubMed: 26199464
- Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-B Protects Rat Cardiac Allografts From Ischemia-reperfusion Injury.PubMed: 26371596
- Dual antiplatelet and anticoagulant APAC prevents experimental ischemia–reperfusion-induced acute kidney injurypubmed:27405618
- Endothelial glycocalyx layer shedding following lung resectionpubmed:27643669
- Resuscitation with Pooled and Pathogen-Reduced Plasma Attenuates the Increase in Brain Water Content following Traumatic Brain Injury and Hemorrhagic Shock in Rats10.1089
- Resuscitation with pooled and pathogen-reduced plasma attenuates the increase in brain water content following traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic shock in rats the rat.doi/10.1089/neu.2016.4574
- Volume kinetics of Ringer's lactate solution in acute inflammatory disease10.1016:j.bja.2018.04.023
- MPO (myeloperoxidase) reduces endothelial glycocalyx thickness dependent on its cationic chargePubmed:29903730
- Plasma resuscitation improved survival in a cecal ligation and puncture rat model of sepsisPubmed:28591008
- Experimental models of endotheliopathy: impact of shock severityPubmed:28697004
- Effects of propranolol and clonidine on brain edema, blood-brain barrier permeability, and endothelial glycocalyx disruption after fluid percussion brain injury in the ratPubmed:28930945
- The Endothelial Glycocalyx in the Peritoneal Microcirculation of Rats with Chronic Kidney Failure Exposed to Dialysis Solutions173015_06.pdf
- Plasma ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in burn injuryDoi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.08.027
- Dexmedetomidine preserves the endothelial glycocalyx and improves survival in a rat heatstroke modelPubmed: 30374889
- Postoperative microcirculatory perfusion and endothelial glycocalyx shedding following cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypassPubmed: 30687934
- Microvascular alterations during cardiac surgery using a heparin or phosphorylcholine coated circuitPubmed: 31787433
- Increased syndecan-1 and glypican-3 predict poor perinatal outcome and treatment resistance in intrahepatic cholestasis: Syndecan-1, glypican-3 and ICPPubmed: 31919038
- Heparin Binding Protein and Endothelial Glycocalyx Markers in Severe COVID-19–A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
- Newly Developed Recombinant Antithrombin Protects the Endothelial Glycocalyx in an Endotoxin-Induced Rat Model of Sepsis33375342
- Effect of liraglutide on microcirculation in rat model with absolute insulin deficiency34119534
- The effect of pre-operative methylprednisolone on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo …34423832
- Inhalation of 2% hydrogen improves survival rate and attenuates shedding of vascular endothelial glycocalyx in rats with heat stroke34524269
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses serum syndecan-1 elevation and improves survival in a rat hemorrhagic shock modelPubmed:35110424
- Resuscitation of hemorrhagic shock using normal saline does not damage the glycocalyx in the immediate resuscitation phase