ELISA Kit DIY Materials for Fibronectin (FN) 
FN1; CIG; FINC; LETS; MSF; GFND2; Anastellin; Migration-Stimulating Factor; Cold-Insoluble Globulin; Large, External, Transformation-Sensitive Protein
- UOM
- FOB US$ 1,166.00 US$ 1,944.00 US$ 3,499.00 US$ 6,804.00 US$ 11,664.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.KSA037Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsMain materials for "Do It (ELISA Kit) Yourself".
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategorySignal transductionInfection immunity
- Reagent Contents Capture Antibody, Detection Antibody, Standard, Streptavidin-HRP, TMB Substrate, 96-well Plate
- Detectable SampleSerum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
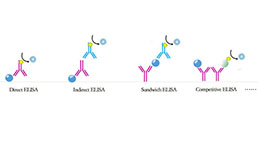
- Applicable PrincipleDouble-antibody Sandwich ELISA for Antigen Detection
- Detectable Range1.56-100ng/mL
- Applicable Sensitivity0.56ng/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The Abs in the kit have high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Fibronectin (FN).No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Fibronectin (FN) and analogues was observed.
Usage
1. Coat the plates with 100μL per well of working solution of Capture Antibody.incubate overnight at 4°C or incubate at 37°C for 2 hours.
2. Aspirate and wash 1 time.
3. Block the plates with 200 μL per well of working solution of Blocking Buffer. Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 hours.
4. Aspirate and wash 1 time. The plates are now ready for sample detection, the protocol is the same as regular ELISA.
Storage
Antibodies, Standard and Streptavidin-HRP should be stored at -20°C. TMB should be stored at 4°C. 96-well Plate could be stored at room temperature. The contents are valid for twelve months. They are stable for one month after opening when stored at 4°C.
Support pack
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Advanced oxidation protein products induce mesangial cell perturbation through PKC-dependent activation of NADPH oxidasePubMed: 19019916
- Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jellyPubmed: 24739658
- Identification of compounds from the water soluble extract of Cinnamomum cassia barks and their inhibitory effects against high-glucose-induced mesangial cells.Pubmed: 24013407
- Bioactive compounds from Cornus officinalis fruits and their effects on diabetic nephropathyScienceDirect: S0378874114002414
- Inhibition by Female Sex Hormones of Collagen Gel Contraction Mediated by Retinal Pigment Epithelial CellsPubmed: 24609629
- Mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation, gene expression and protein production in human platelet-rich plasma-supplemented mediaPubmed:Pmc4130592
- Metabolic and cytoprotective effects of in vivo peri-patellar hyaluronic acid injections in cultured tenocytesPubmed:25333747
- Establishing principles of macromolecular crowding for in vitro fibrosis research of the vocal fold lamina propriaPubmed:25545625
- In vivo bioengineered ovarian tumors based on collagen, matrigel, alginate and agarose hydrogels: a comparative studyPubmed:25634132
- In vivoPubMed: 25634132
- Impact of Nigella Sativa, Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Chromium Picolinate onNF-κB/leptin-insulin Axisin Obese Subjects with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseAjmbr: 3
- Comparative proteomics of milk fat globule membrane in goat colostrum and mature milkPubmed:27173528
- Maternal endothelial damage as a disorder shared by early preeclampsia, late preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.pubmed:27865093
- Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on efficacy and hemorrhagic transformation of rt-PA intravenous thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic strokeArticle_en:CJFDTotal-XDJB201611014
- Serum fbronectin distinguishes the early stages of hepatocellular carcinomapubmed:28842594
- Pigment epithelium‑derived factor protects human glomerular mesangial cells from diabetes via NOXO1‑iNOS suppression10.3892/mmr.2017.7563
- Tenomodulin is essential for prevention of adipocyte accumulation and fibrovascular scar formation during early tendon healing.pubmed:29022912
- Effects of panax notoginseng saponin on the pathological ultrastructure and serum IL‐6 and IL‐8 in pulmonary fibrosis in rabbitsPubmed:29932250
- Corn silk (Zea mays L.), a source of natural antioxidants with α-amylase, α-glucosidase, advanced glycation and diabetic nephropathy inhibitory activitiesPubmed: 30530231
- Impact of Hydrogel Elasticity and Adherence on Osteosarcoma Cells and OsteoblastsPubmed: 30838809
- TNF-α Regulates ITGβ1 and SYND4 Expression in Nucleus Pulposus Cells: Activation of FAK/PI3K SignalingPubmed: 31111299
- Three kinds of corneal host cells contribute differently to corneal neovascularization
- Effects of autophagy on macrophage adhesion and migration in diabetic nephropathyPubmed: 31352855
- Growth hormone induces Notch1 signaling in podocytes and contributes to proteinuria in diabetic nephropathyPubmed: 31511328
- Fabrication and Evaluation of a Xenogeneic Decellularized Nerve-Derived Material: Preclinical Studies of a New Strategy for Nerve RepairPubmed: 31758411
- Molecular hydrogen regulates PTEN‐AKT‐mTOR signaling via ROS to alleviate peritoneal dialysis‐related peritoneal fibrosisPubmed: 31930571
- Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Th-Cell-Related Cytokines Released after Progressive EffortPubmed: 32210109
- Are the Circulating Levels of Copeptin and Fibronectin Dysregulated in Preeclamptic South African Black Women?
- Advanced glycation end-products associate with podocytopathy in type II diabetic patients
- Early mobilization in spinal cord injury promotes changes in microglial dynamics and recovery of motor functionPubmed:35586775